JUBA, South Sudan: Thousands of civilians in towns and villages across Sudan have been forced to flee in recent weeks to escape the worsening conflict in the country, which has entered its second bloody month, leading to fears of a new global refugee crisis.
Initial clashes between former allies the Sudanese Armed Forces and paramilitary group the Rapid Support Forces have escalated into heavy combat, displacing hundreds of thousands of people from their homes.
Hospitals have been overwhelmed by the numbers of wounded, and disruptions to basic utilities and shortages of medical supplies have forced medical staff to turn away even the critically ill.
Meanwhile, shortages of food, fuel, electricity and clean water, coupled with economic collapse and the breakdown of law and order, have forced entire communities to pack up and leave in search of security and relief.
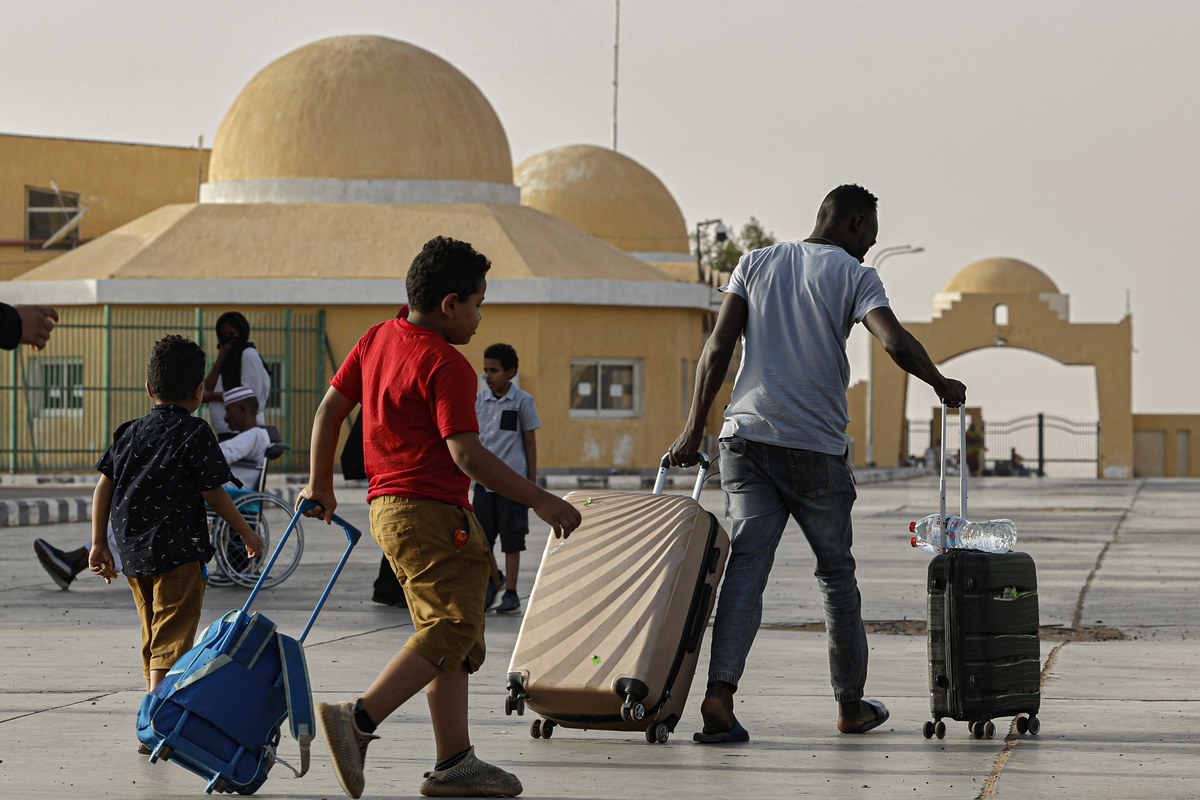

Passengers fleeing war-torn Sudan cross into Egypt through the Argeen Land Port on May 12, 2023. (AFP)
In the first four weeks of the crisis, around 200,000 people fled Sudan while another 700,000 were displaced inside the country. As many as 860,000 refugees and returnees are expected by the UN refugee agency UNHCR to flee by October, raising fears among European policymakers of a new influx of migrants over the coming months..
Europe was forced to confront the issue of mass migration in 2015, when hundreds of thousands of people fleeing war, poverty and persecution in Africa, the Middle East and Asia began arriving from across the Mediterranean.
More recently, the continent has absorbed millions of Ukrainians fleeing the Russian invasion, which has placed additional strain on a continent already grappling with high energy prices as a result of gas shortages.
However, few experts predict Europe will see anything close to the same number of migrants as a result of the crisis in Sudan. Instead, most expect the majority to be displaced internally or settle in neighboring African states.
“Some of the refugees will try to go to Europe, but I don’t see that there will be mass migration going to Europe right now,” Namira Negm, director of the African Migration Observatory in Morocco, told Arab News.
“It will increase but it will not be mass migration. Migration to neighboring countries needs to be addressed first.”
INNUMBERS
- 116,995 First-time asylum seekers from Sudan in EU+ area during 2015 peak.
- 860,000+ Refugees and returnees expected to flee Sudan by Oct. (UNHCR).
- $445m Funding required to support the displaced until Oct. 2023 (UNHCR).
Nevertheless, many in Europe remain fearful that any fresh influx will place additional strains on the resources of host nations, and trigger a surge in anti-immigrant sentiments and support for right-wing populist movements.
In response to previous waves of migration several European nations adopted draconian immigration policies, making it more difficult for new arrivals to obtain asylum and the right to remain. Those who still try to reach Europe face dangerous journeys, including sea voyages in often flimsy and overloaded vessels.
“Reaching Europe would require navigating treacherous and expensive migration routes, often involving perilous sea crossings and facing the risk of exploitation and abuse by human traffickers,” Franck Duvell, a senior researcher at Universitat Osnabruck in Germany, told Arab News.
“Numbers might go up a little, but I don’t see these networks and routes now. Traveling to western Libya has become dangerous and is getting more and more difficult, and therefore (an) increasing number of people actually continue their journey to Tunisia.
“I don’t see Sudanese traveling all the way to Tunisia. It’s simply too far, it’s too expensive, it’s too dangerous … Even if numbers are increasing, the total numbers will still be relatively small.”
Migrant numbers were already on the rise prior to the start of the conflict last month. More than 36,000 people arrived from Sudan in Europe’s Mediterranean region between January and March, nearly twice the number compared with the same period in 2022, according to the latest UNHCR figures.
Sudan has been caught in a cycle of violent coups and countercoups for years. The latest, in October 2021, resulted in a transitional, civilian-led government being overthrown by a military junta led by the two factions now fighting each other.
Since the start of a shaky political transition in 2019, after long-time autocratic ruler Omar Al-Bashir was ousted, Sudan has been plagued by political and economic instability, prompting many citizens to seek sanctuary outside the country.
According to the EU’s European Asylum Support Office, Sudanese nationals represented the fifth-largest group of applicants for international protection in the EU in 2020, with more than 34,000 new applications. This was a significant increase on the previous year, when there were about 18,000 new applications.
An economic crisis, including high inflation, devaluation of the national currency and shortages of basic goods, had already caused poverty and unemployment to increase in Sudan prior to the latest conflict, which began on April 15.
And it is not only the Sudanese people themselves who face displacement. Before the fighting began, Sudan hosted more than a million refugees, 300,000 of them in the capital Khartoum, who had fled South Sudan, Ethiopia and Eritrea. Many of them are now returning home or looking for refuge elsewhere in the region or further afield.
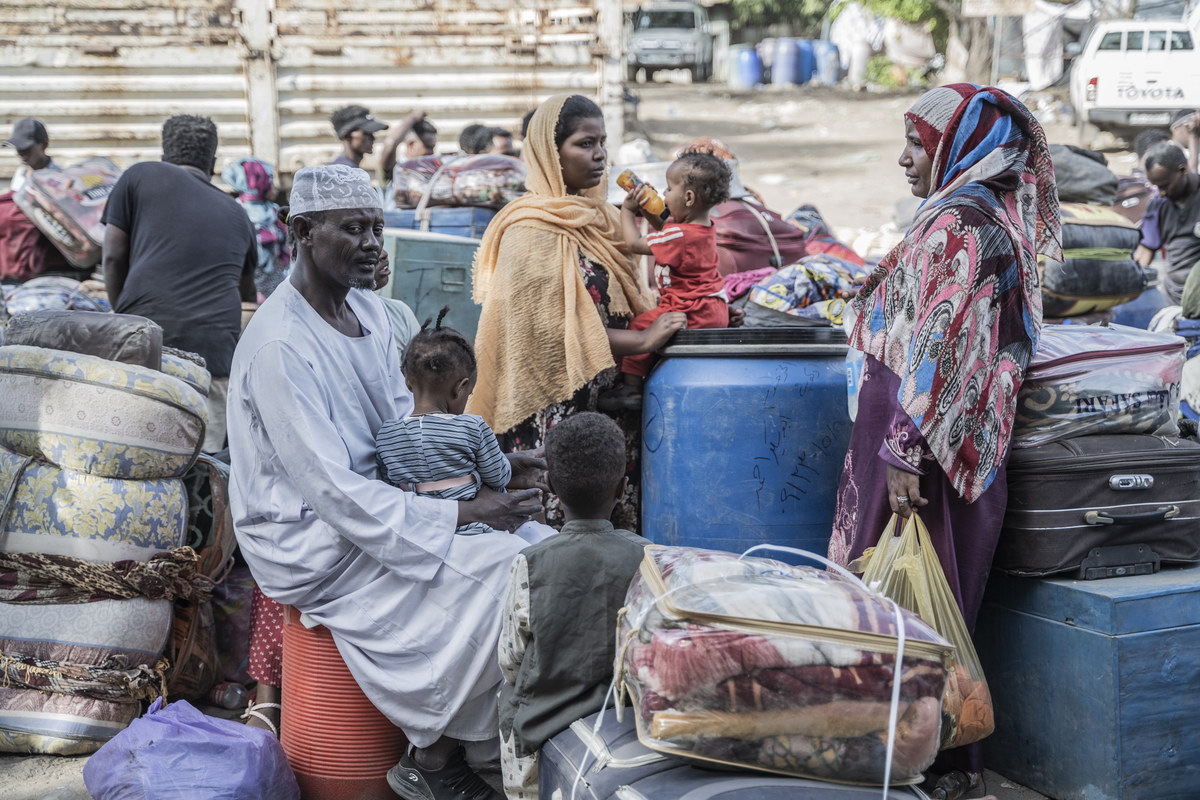
Refugees from Sudan who crossed into Ethiopia rest in Metema, on May 5, 2023. (AFP)
If the crisis in Sudan becomes long drawn out, akin to the Syrian civil war, the possibility of large number of Sudanese refugees seeking safety in Europe cannot be ruled out.
“A protracted conflict could create unwanted uncertainties,” Thirsa de Vries, a Sudan expert at the Dutch peace organization PAX, told Arab News.
“This is why it is also important that the international community (engages with) the different actors that might be involved, or works with neighboring countries to close corridors for weapons smuggling.”
The possibility of a large number of Sudanese refugees attempting to reach Europe also highlights the importance of cooperation between nations in managing migration flows.
Abdullahi Hassan, a researcher at human rights organization Amnesty International who specializes in Sudan, stressed the importance of ensuring the security and stability of host and origin countries.
“With adequate planning and resources, it is possible to provide safe and orderly routes for those seeking refuge,” he told Arab News.
He said the response to the crisis in Sudan should not solely focus on migration and added: “It must instead prioritize the protection of civilians and access to humanitarian aid.
“The EU and its member states should use their influence, both in the region and in Sudan, to ensure that they are directly engaging with the parties to the conflict to protect civilians and civilian infrastructure, encourage immediate and unrestricted access for humanitarian actors, and pressure the Sudanese authorities to allow safe exit passages for people trying to flee the conflict.”
As the fighting continues to rage, the warring Sudanese factions have held talks in Saudi Arabia to discuss a ceasefire but made it clear they would not negotiate an end to the conflict.
Despite the challenges posed by the violence, humanitarian organizations are working to provide aid to those affected by the Sudan crisis. But attacks on aid workers and the looting of relief supplies have made it increasingly difficult for agencies to deliver help to needy communities, which could in turn affect the response of donor countries.
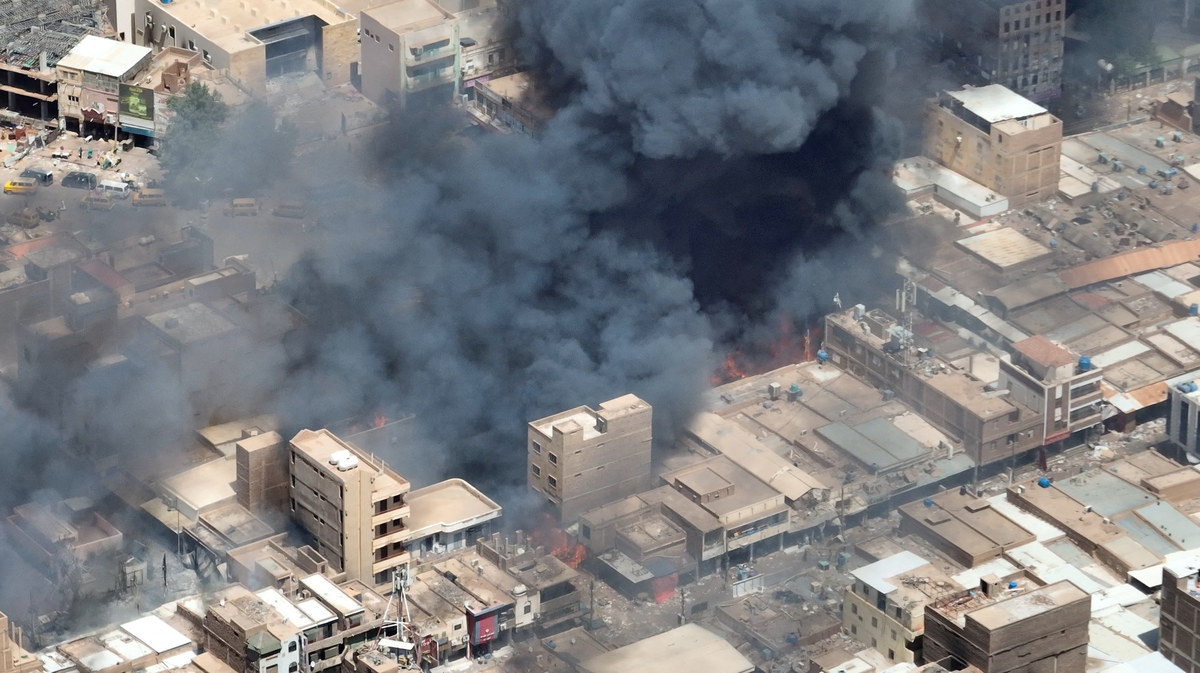

A view shows black smoke and fire at Omdurman market in Omdurman, Sudan, May 17, 2023. (Screengrab/Reuters)
Some organizations “have evacuated international staff, particularly those that were in the most affected areas,” UNHCR spokesperson Faith Kasina, told Arab News, who highlighted the risks and limitations of aid provision during armed conflicts.
The UN’s Children’s Fund, UNICEF, reported on May 5 that at least 190 children have been killed and 1,700 injured since the fighting began in Sudan. While a tentative ceasefire allowed foreign nations to evacuate their citizens from the country in the past few weeks, Sudanese nationals continue to endure great hardships.
Several media outlets, including the BBC, the Washington Post and Al-Jazeera, have interviewed Sudanese citizens who said their passports were locked inside foreign embassies, leaving them trapped in their own country.
Hassan, the Amnesty International researcher, said foreign nations must provide safe evacuation procedures, and that the warring factions must “stop attacking humanitarian aid workers.”
But he added that instances of attacks on workers and the looting of aid supplies “should not be an excuse to withdraw funding.”
“The response to the crisis in Sudan is completely different from the response, for example, Ukraine received when the conflict started in that country,” said Hassan.
“European countries should, nevertheless, provide safe and regular pathways to Europe for those seeking international protection … It is the responsibility of the EU and member states to ensure that such pathways are made available.”
However, public sentiment in Europe appears to be overwhelmingly hostile to refugees. Both Italy and the UK have faced recent criticism for their strict immigration policies, which aid agencies warn could drive more refugees into the arms of smuggling gangs.
In mid-April, Italy passed legislation to curb undocumented migration, including tougher sentences for those convicted of human trafficking and terminating residency permits for migrants who face humanitarian risks.
This drew criticism from search-and-rescue organizations, who warned it would lead to more deaths at sea in the Mediterranean as migrants seek illegal routes to Europe.
The British government has been accused of racial discrimination in its refugee policy. Immigration experts point out that although hundreds of thousands of visas were provided for Ukrainian refugees, there is no plan, or safe route, to help those fleeing violence in Sudan.
Ultimately, the best way to avoid migrant crises is by helping ensure that all countries in Africa are able to offer their citizens a decent quality of life.
“The root cause is lack of development; people lose hope in their country and end up migrating to other countries,” African Migration Observatory Director Negm said regarding the importance of stability in Africa.
“If they have a good life in their own home countries, they will not think of going somewhere else.”






















