LONDON: You cannot see it with the naked eye but high over your head, just above the altitude at which the highest-flying passenger jets cruise, there is a fragile layer of naturally occurring gas that shields all life on Earth from the deadly effects of the ultraviolet radiation emitted by the sun.
This is the ozone shield, a belt of gas — specifically ozone, or O3, which is made of three oxygen atoms — formed by the natural interaction of solar ultraviolet radiation with O2, the oxygen we breathe.
Without it, we’d all be cooked. In the words of the UN Environment Program’s Ozone Secretariat, “long-term exposure to high levels of UV-B threatens human health and damages most animals, plants and microbes, so the ozone layer protects all life on Earth.”
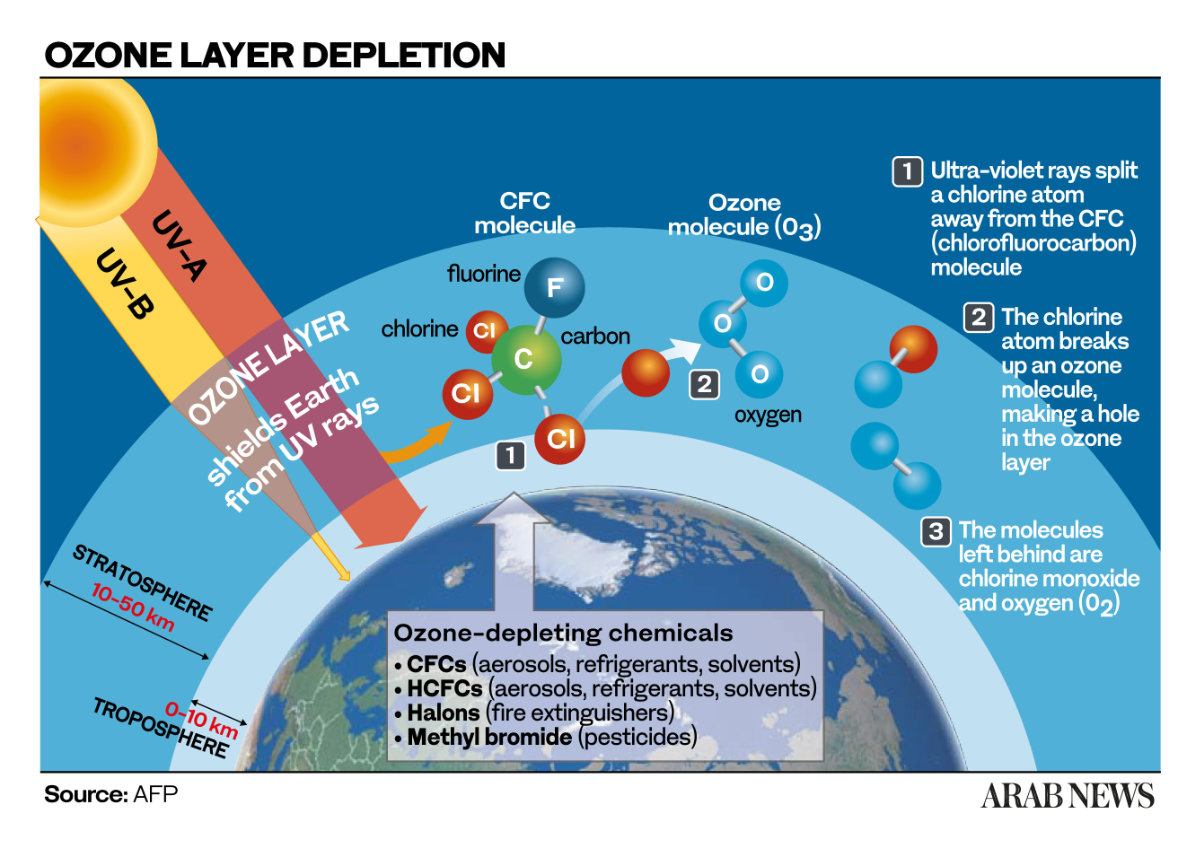
But now, after decades of battling to save it — and us — scientists have announced that the hole in the ozone layer, which was detected in the 1980s, is healing.
The announcement this month is a victory for one of the greatest international scientific collaborations the world has ever seen. And, as the world struggles to tackle climate change, it is a timely and hugely encouraging demonstration of what the international community can achieve when it really puts its mind to something.
As the nations of the world prepare to gather at the UN Climate Change Conference, COP28, in the UAE, where in November they will be expected to account for the progress they have made toward the climate-change goals set by the 2015 Paris Agreement, the brilliant success of the ozone-saving 1987 Montreal Protocol can only be an inspiration.

A scientist launches a research balloon at Australia’s Giles Weather Station. (Shutterstock)
The ozone layer, and its role in absorbing the sun’s ultraviolet radiation, was first identified by two French physicists, Charles Fabry and Henri Buisson, in 1913, but it was not until 1974 that an article in the journal Nature warned that we were in danger of destroying it.
Chemists F. Sherwood Rowland, of the University of California Irvine, and Mario Molina, of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, discovered that human-created gases, such as the chlorofluorocarbons, or CFCs, used in appliances and products such as fridges and aerosols, were destroying ozone.
In 1995, Rowland and Molina, together with Dutch scientist Paul Crutzen, were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry “for their work in atmospheric chemistry, particularly concerning the formation and decomposition of ozone.”
 But, the Nobel citation continued, “the real shock came” in 1985, when scientists with the British Antarctic Survey, which had been monitoring the Antarctic ozone layer since 1957, detected “a drastic depletion of the ozone layer over the Antarctic.”
But, the Nobel citation continued, “the real shock came” in 1985, when scientists with the British Antarctic Survey, which had been monitoring the Antarctic ozone layer since 1957, detected “a drastic depletion of the ozone layer over the Antarctic.”
The size of the hole identified over the survey’s Halley and Faraday Antarctic research stations seemed to vary, which at first was a puzzle.
It is now understood, the BAS explains, “that during the polar winter, clouds form in the Antarctic ozone layer and chemical reactions in the clouds activate ozone-destroying substances.
“When sunlight returns in the spring, these substances — mostly chlorine and bromine from compounds such as CFCs and halons — take part in efficient catalytic reactions that destroy ozone at around 1 percent per day.”
The discovery “changed the world.” NASA satellites were used to confirm that “not only was the hole over British research stations, but it covered the entire Antarctic continent.”
This was the so-called “ozone hole” and, as Crutzen noted in his 1995 Nobel lecture, “it was a close call.”
He said: “Had Joe Farman and his colleagues from the British Antarctic Survey not persevered in making their measurements in the harsh Antarctic environment … the discovery of the ozone hole may have been substantially delayed and there may have been far less urgency to reach international agreement on the phasing out of CFC production.”
It was the work of the survey that led to the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, an agreement, adopted in 1987, that regulated the production and consumption of nearly 100 man-made chemicals identified as “ozone depleting substances.”
“There had been suggestions in the 1960s and 1970s that you could put gases into the atmosphere which would destroy ozone,” atmospheric scientist Professor John Pyle, former head of chemistry at the University of Cambridge and one of the four international co-chairs on the Scientific Assessment Panel for the Montreal Protocol, told Arab News.
“At the time there was also concern about the oxides of nitrogen from high-flying supersonic aircraft, such as Concorde, which could destroy ozone.
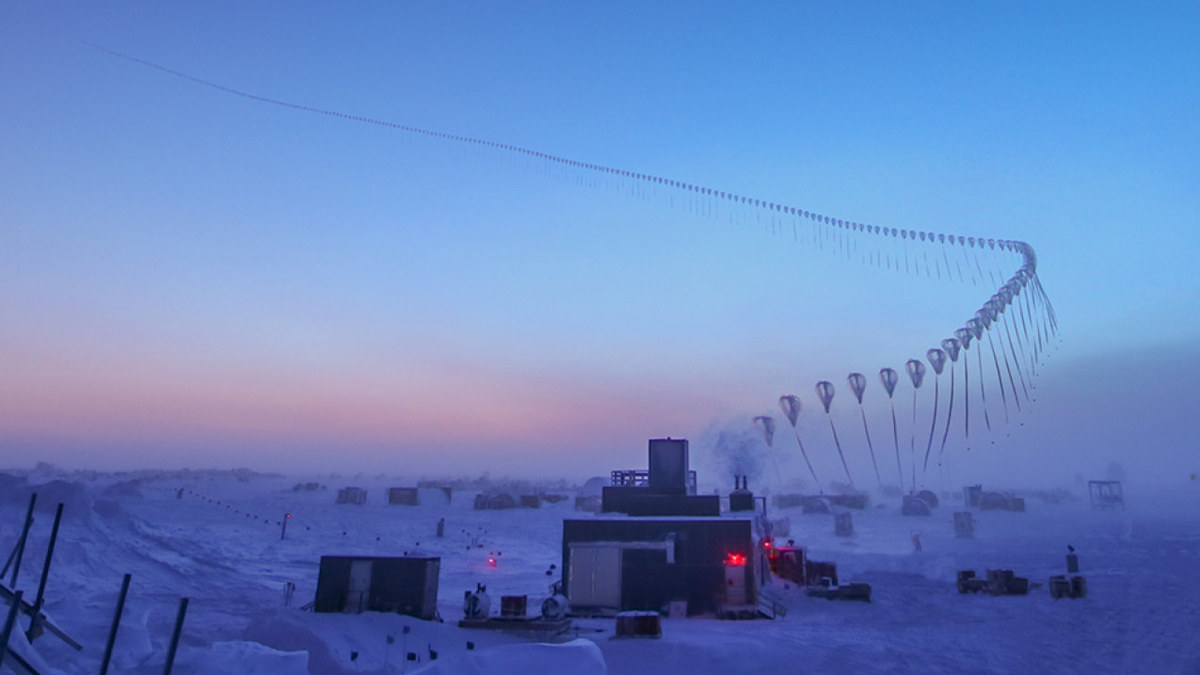

This time-lapse photo shows the path of an ozonesonde as it rises into the atmosphere in the South Pole. (Courtesy of Robert Schwarz/South Pole, 2017)
“But after Rowland and Molina published their paper, suggesting that CFC gases could get high enough up into the atmosphere to destroy ozone, there was about a decade during which this was just a theoretical idea before, thanks to the British Antarctic Survey, the ozone hole was discovered.”
The global reaction, choreographed by the UN and the World Meteorological Organization, was almost startlingly rapid.
The British Antarctic Survey paper was published in 1985, and by 1987 the Montreal Protocol had been agreed. In the words of the UN Environment Program: “The protocol is considered to be one of the most successful environmental agreements of all time.
“What the parties to the protocol have managed to accomplish since 1987 is unprecedented, and it continues to provide an inspiring example of what international cooperation at its best can achieve.”
Without doubt, millions of people have lived longer, healthier lives thanks to the Montreal Protocol. In 2019, the US Environmental Protection Agency estimated that in the US alone the protocol had prevented 280 million cases of skin cancer, 1.6 million deaths, and 45 million cases of cataracts.
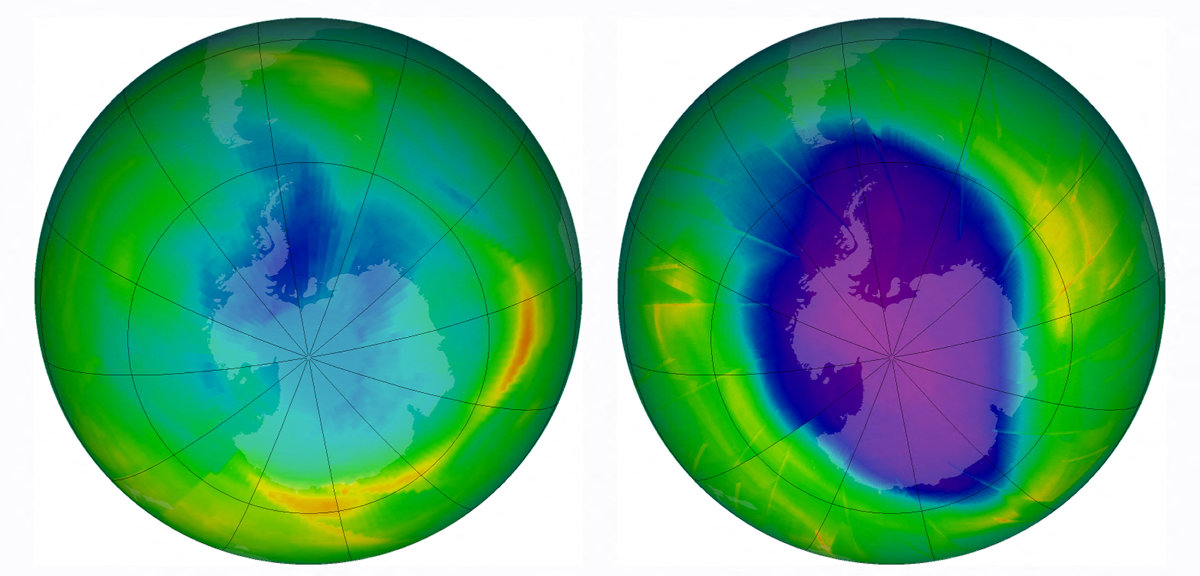
Combo image released by NASA's Earth Observatory on Dec. 1, 2009, showing the size and shape of the ozone hole each year in 1979 (L) and in 2009. (AFP file)
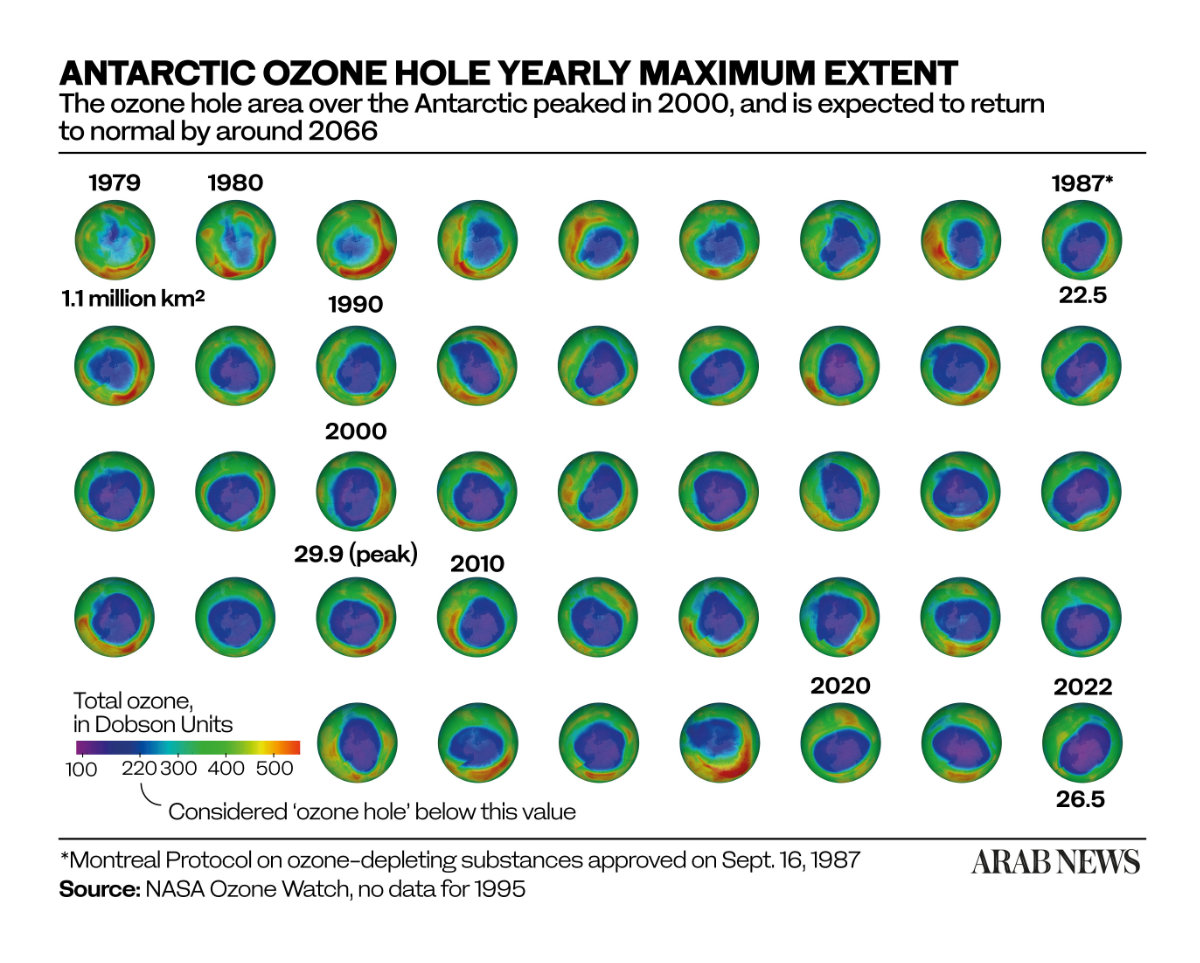
The battle is not over, however. It will take another four decades for the ozone layer to fully recover, according to the latest four-yearly report from the UN-backed Scientific Assessment Panel to the Montreal Protocol on Ozone Depleting Substances, which was published this month.
But according the “Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2022” report: “The phase out of nearly 99 percent of banned ozone-depleting substances has succeeded in safeguarding the ozone layer, leading to notable recovery of the ozone layer in the upper stratosphere and decreased human exposure to harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun.”
If current policies remain in place, it adds, “the ozone layer is expected to recover to 1980 values” — that is, before the appearance of the ozone hole — “by around 2066 over the Antarctic, by 2045 over the Arctic, and by 2040 for the rest of the world.”
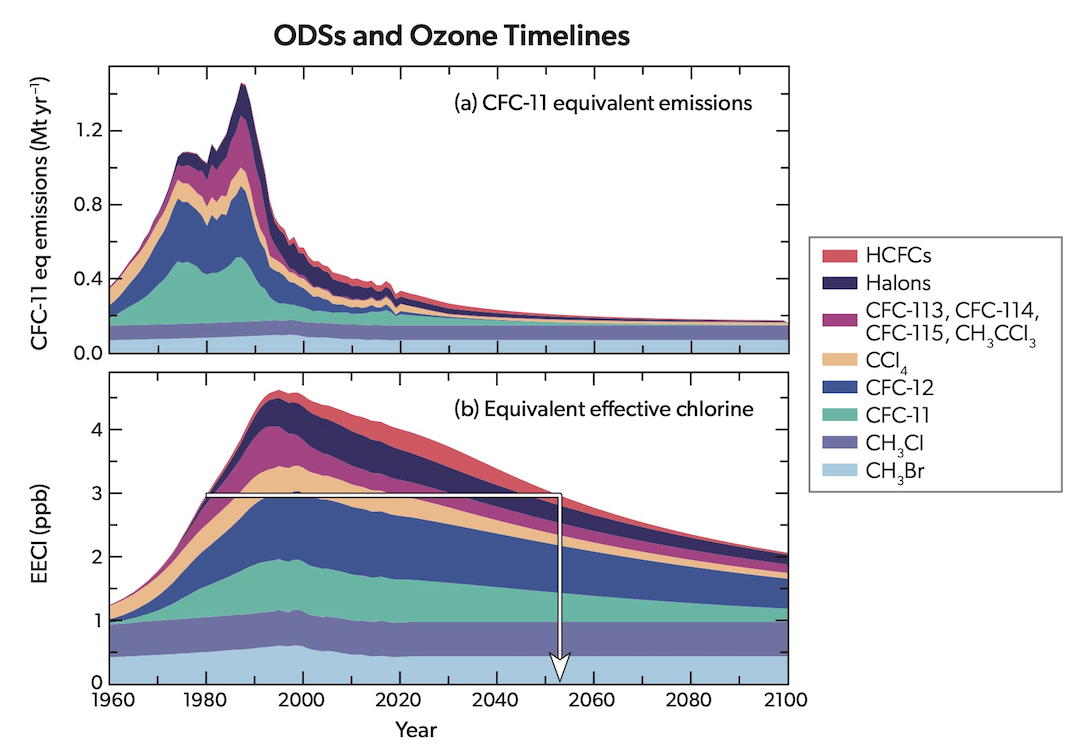
Ozone timelines from the UNEP's Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion report of 2022.
This is “fantastic news,” Meg Seki, executive secretary of the UN Environment Program’s Ozone Secretariat, told Arab News. And it has had an additional benefit in the fight against global warming.
In 2016, an additional agreement, known as the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol, resulted in the scaling down of production and consumption of hydrofluorocarbons, or HFCs, the compounds that were introduced to replace banned CFCs but which were found to be powerful climate change gases. It is estimated that by 2100, the Kigali Amendment will have helped to prevent up to 0.5 degrees Celsius of global warming.
“The impact the Montreal Protocol has had on climate-change mitigation cannot be overstressed,” said Seki. “Over the past 35 years, the protocol has become a true champion for the environment.”

Delegates converse during the 28th meeting of the Parties to the Montreal Protocol in Kigali, Rwanda, on Oct. 13, 2016. (AFP file)
It is also a shining example of what could be achieved in the battle against climate change.
Sept. 16 each year is the UN’s International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer. As Antonio Guterres, the UN’s secretary-general, said as he marked the occasion in 2021: “The Montreal Protocol … has done its job well over the past three decades. The ozone layer is on the road to recovery.”
He added: “The cooperation we have seen under the Montreal Protocol is exactly what is needed now to take on climate change, an equally existential threat to our societies.”





























