DUBAI: When Russian tanks trundled into Ukraine on Feb. 24, alarm bells started ringing in places even far away from the war zone. It transpired that many countries depended heavily on the two warring parties for their wheat supplies, with Arab states of the Middle East and North Africa region figuring prominently on the list.
Which is partly why, for the governments of Lebanon, Egypt, Tunisia, Yemen, and Sudan as well as international aid agencies, the conflict in Ukraine has felt much closer than what the geographical distance between the biggest consumers and the producers of Black Sea grain suggests.
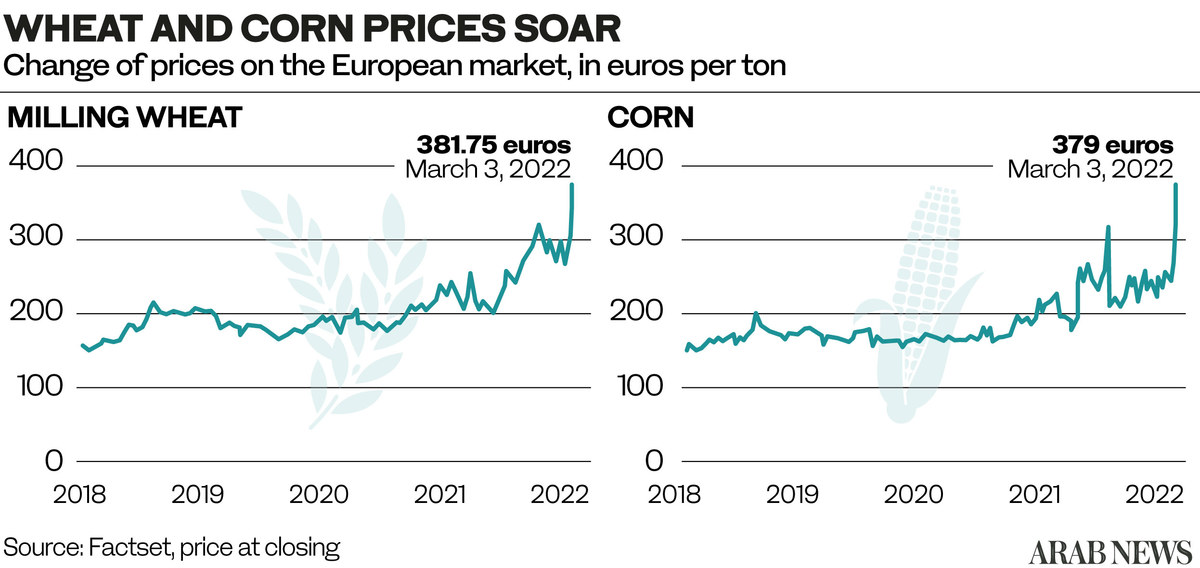
Within days, the fighting had restricted the capacity of both Russia and Ukraine to continue exporting wheat to one of their biggest markets, which depends on the lower-priced Black Sea grain for a major source of its staple foods.
Ukraine has closed several of its ports and the movement of vessels in the Sea of Azov has been ordered to cease until further notice. The effect has been immediate.
MENA states that had already been experiencing food shortages owing to higher import costs, fiscal deficits, and conflict now face an added challenge. Any suspension or reduction of wheat supplies from Ukraine and Russia will deprive citizens of some of the world’s most food-insecure countries of the ability to produce bread and other daily essentials.
Besides being major players in such industries as computer chips, petroleum, wood, grains and sunflower oil, Russia and Ukraine together account for more than 14 percent of global wheat exports and a similar percentage of the world’s corn market.

A combine harvesting picks up the wheat on a field near the Krasne village in the Chernihiv area, north from Kiev, on July 05, 2019. (Anatolii Stepanov / FAO / AFP)
Russia is the world’s top wheat exporter and Ukraine the fourth, according to estimates by the US Department of Agriculture. Russia, Ukraine and Belarus are also among the world’s leading fertilizer exporters.
Reuters has reported, quoting traders and bankers, that the war has halted shipping from Ukraine’s ports, while financial sanctions have put payments for purchases of Russian wheat in doubt, piling additional risk onto the shoulders of MENA governments.
“Everyone is looking for other markets as it is becoming increasingly impossible to buy stocks from Ukraine or Russia,” one Middle Eastern commodities banker said, citing shipping disruptions, new economic sanctions, and rising insurance premiums. “The market is not expecting Ukrainian and Russian exports to resume until the fighting ends.”
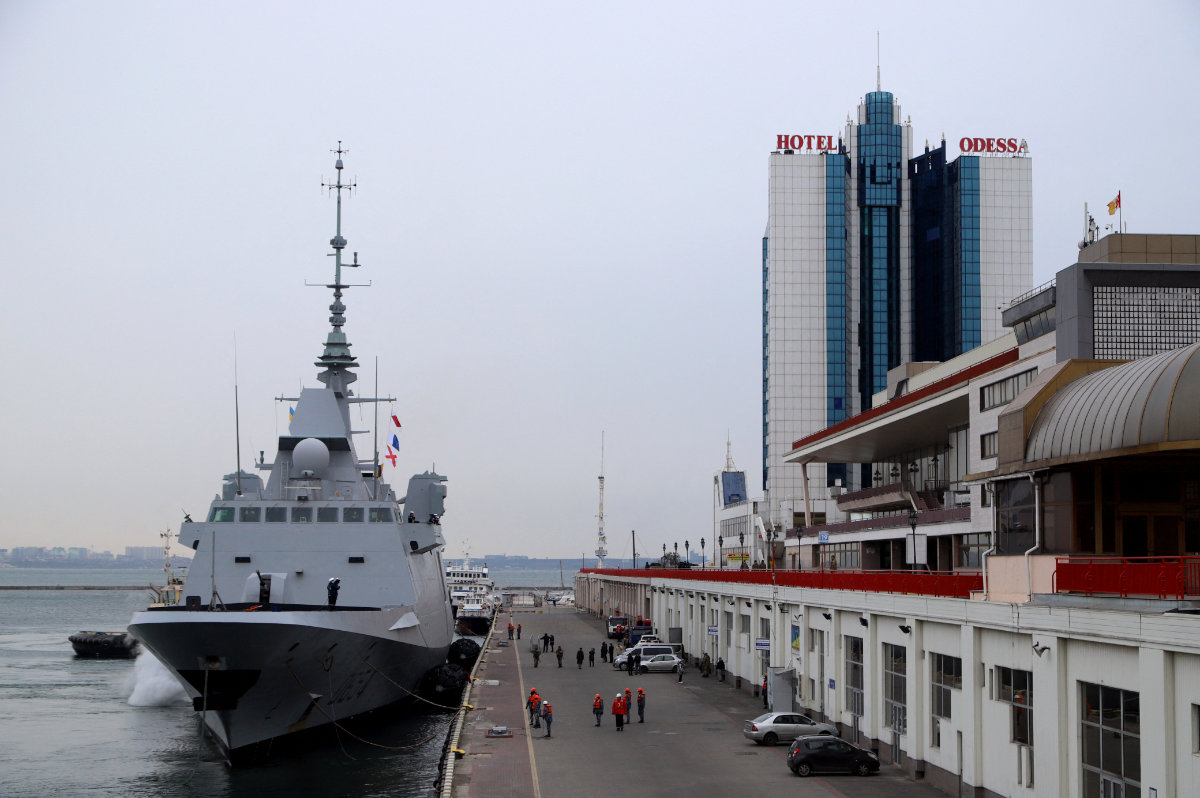

The sea port of Ukraine's Black Sea city of Odessa, where the country's grain supplies are shipped to foreign countries, has been closed because of the Russian invasion and grain supplies, threatening the food supplies of various countries. (Photo by Oleksandr Gimanov / AFP)
In Lebanon, officials expect wheat stocks to run out in a month. In Yemen, which imports 90 percent of its wheat, there is outright panic. Years of drought have created near famine conditions and left the bulk of Yemen’s population dependent on food aid. The situation has worsened since the 2014 Houthi takeover of the capital Sanaa.
Last year, Ukraine was the second-largest supplier of wheat to the UN’s World Food Program, with much of the aid going to Syria, where nine out of 10 of the country’s pre-war population are now on, or below, the poverty line, according to the UN.
David Beasley, the WFP’s executive director, said a lack of funding had forced the WFP to halve rations for 8 million civilians, with further sharp reductions to follow. “And just when you think that’s bad enough, we’ve got a war now in Ukraine,” he added in a video posted on the food organization’s website.
“We get 50 percent of our grains out of the Ukrainian and Russian area. It is going to have a dramatic impact on food, oil, and shipping costs. Just when you think it couldn’t get worse, it’s going to get worse. It’s a catastrophe on top of catastrophe here. It’s just heartbreaking.”
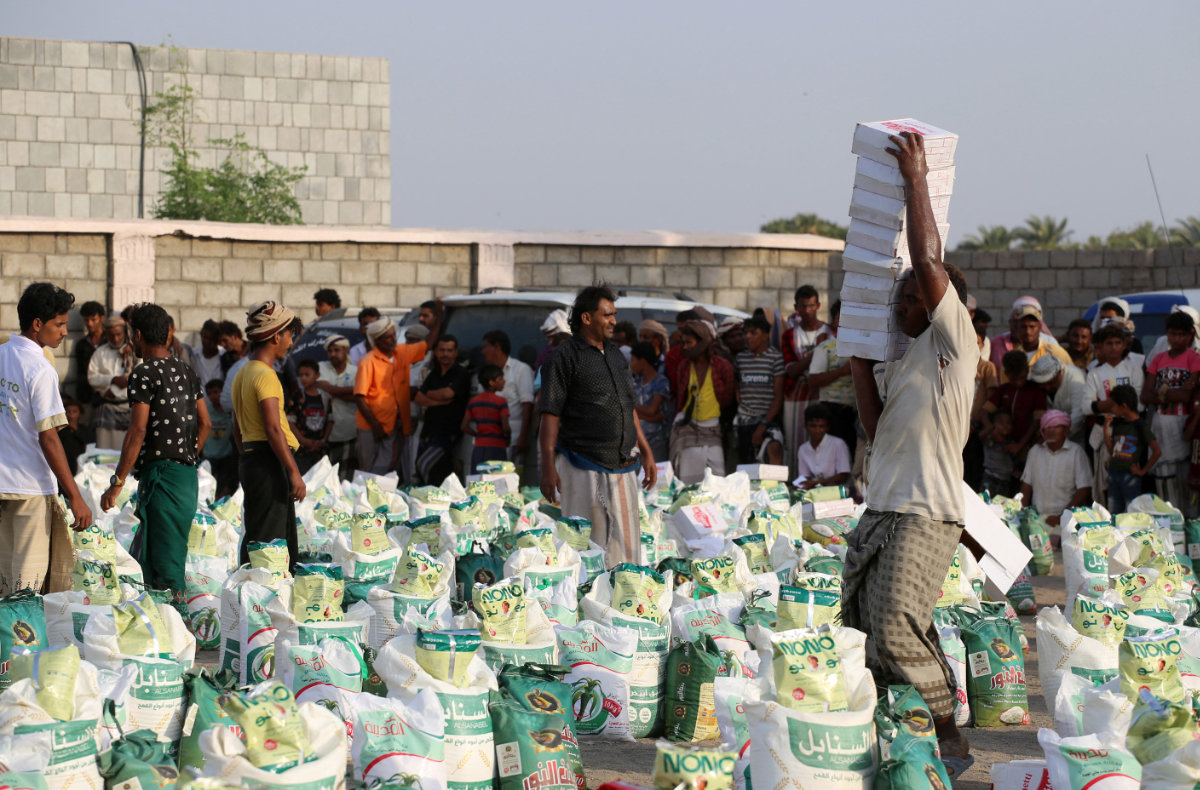

People displaced by conflict receive food aid to meet their basic needs at a camp in the Khokha district of Yemen's war-ravaged western province of Hodeidah, on Jan. 14, 2022. (Khaled Ziad / AFP)
In Lebanon, images of an imminent food crisis were seared into the nation’s memory by the explosions that destroyed the port of Beirut in August 2020. While Lebanon has found a new storage site for imported wheat, it must now find new sources of wheat supplies.
Lebanese Minister of Economy and Trade Amin Salam noted that Lebanon imported around 60 percent of its wheat from Ukraine and Russia, and said the government had opened talks with France, India, and the US with the aim of sourcing wheat from them instead, but at a higher cost.
FASTFACT
Ukraine has banned exports of rye, buckwheat, millet, barley, sugar, salts, meats until end of 2022.
“I couldn’t buy a croissant or a manoushe today,” Elio Alam, a resident of Beirut, told Arab News on Thursday, referring to a popular Lebanese street food. “I stopped at many shops, and all of them said they were not producing the products to save flour for making bread. But even bread is missing at several bakeries.”
Given the parlous state of Lebanon’s economy, the concerns are twofold: From where the government can now source supplies and how it can pay for them. “The actual Lebanese public finance situation is far from clear due to the total lack of professionalism in managing it. It is consequently impossible to determine if there are still resources within the state treasury,” Riad Saade, president of CREAL, an agricultural research center and consultancy company in Beirut, told Arab News.
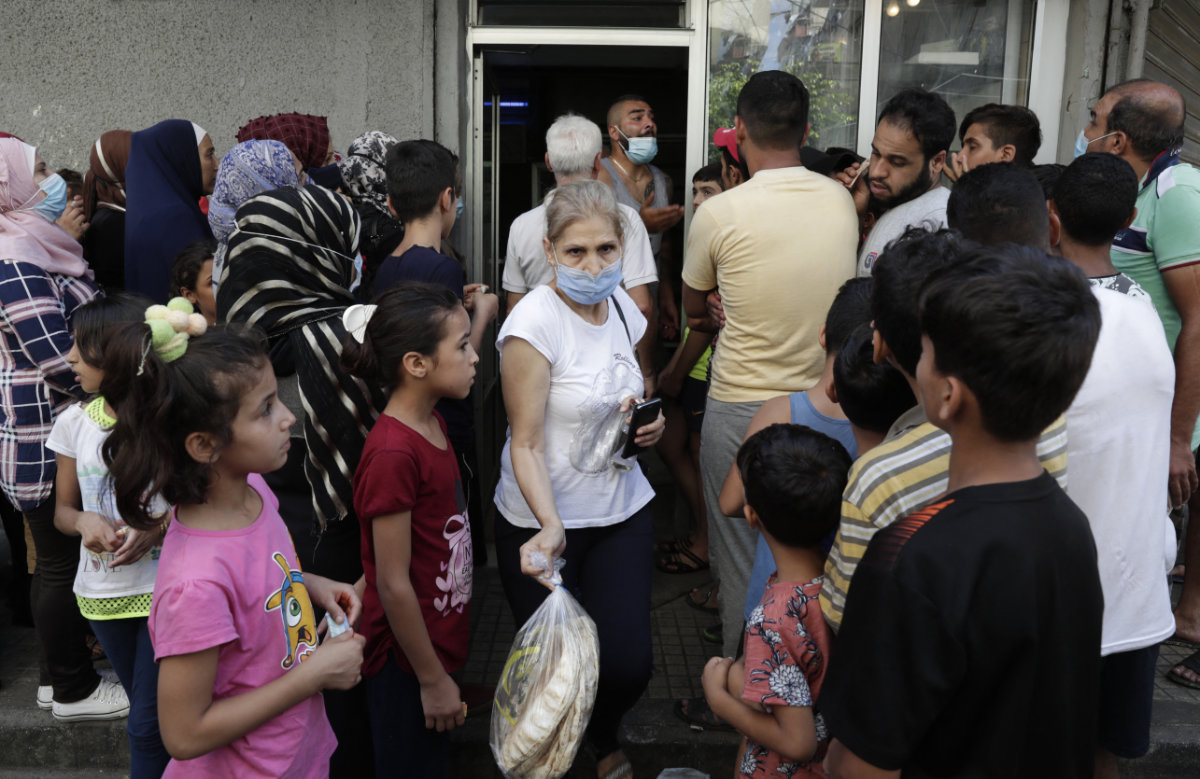

People queue at a bakery in the neighborhood of Nabaa in Lebanon amidst a wave of shortages of basic items due to a severe economic crisis. (AFP file photo)
“Officials might still find ways to secure financing for wheat subsidies from other budget allocations. They will also seek donations, which will have political ramifications. The US and France might consider supporting the Lebanese population. The WFP might also have a role.
“The international market is open and accessible. It is a matter of financing the procurement and dealing with the price, which has risen because of the crisis. Australia and Kazakhstan can also be sources of supply.”
Saade, who did not rule out the possibility of bread riots and civil unrest, said: “We might have reached the situation where people will have no other choice but to revolt.”
In common with Lebanon, officials of other cash-strapped MENA governments have been scrambling to secure alternative grain supplies at affordable prices.
Syrian regime officials held an emergency meeting after the invasion began to take stock of national reserves of grain, sugar, cooking oil, and rice. Syrian President Bashar Assad’s ministers are reportedly considering reducing prices of some basic goods in local markets and rationing oil for the next two months.
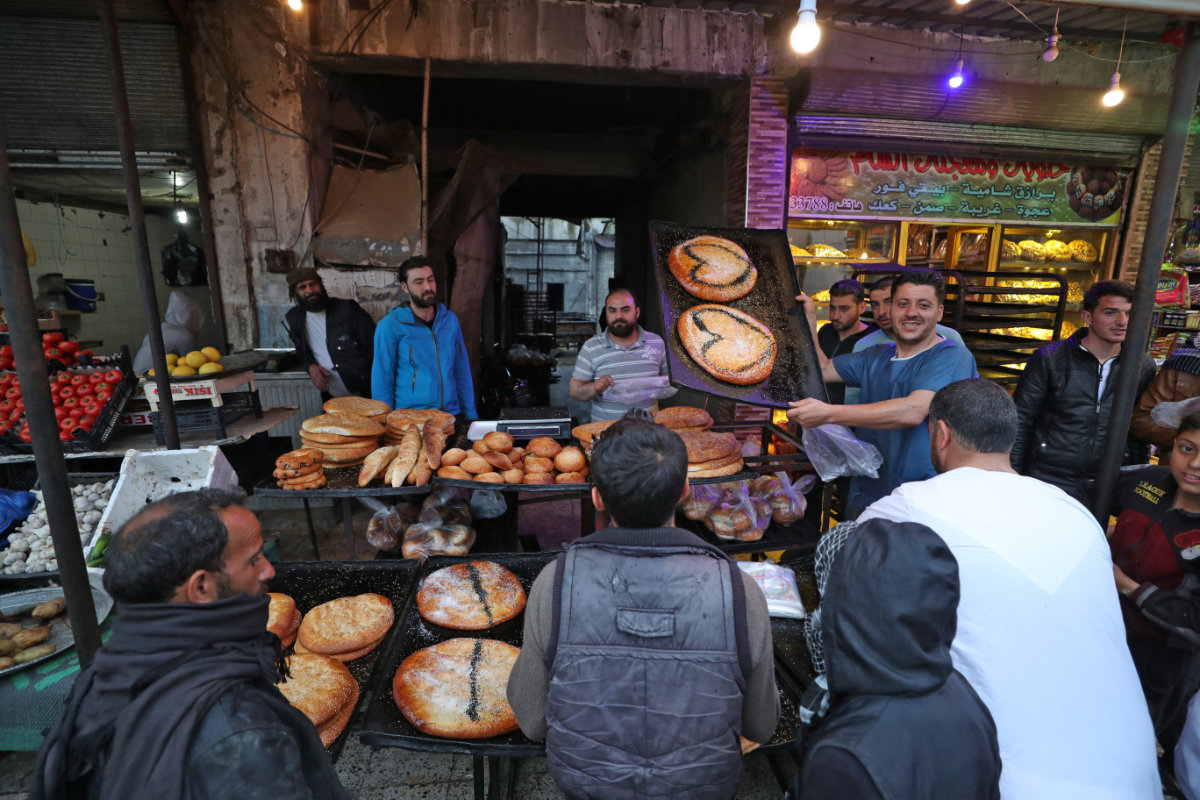

People queue up outside a bakery in Syria's northwestern city of Idlib on April 24, 2020. (OMAR HAJ KADOUR / AFP)
On top of existing austerity measures, any cutbacks would pile more stress and financial strain on Syrians living in regime-controlled territories. As for those living in rebel-held or Kurdish-administered areas of the country, they depend heavily on cross-border trade with Turkey, Iraq, and Lebanon, which have chronic supply issues of their own.
In rebel-held Idlib, one of the most food-deprived pockets of the Middle East, Omar Karim, a laborer and father of three, said his family was “already living on the brink of starvation every day.”
Having lived under Russian and Assad-regime bombardment for many years, Karim fears his family will soon suffer the ripple effect of another Russian war.
“Russia managed to stomp on us and is waging war inside and outside of Syria,” Karim told Arab News. “I don’t know how I’ll manage to keep feeding my family. What will we eat? Grass?”
Egypt, too, is sensing danger ahead. Analysts believe the war in Ukraine could pose a serious threat to the country’s economy, with the price of wheat rising almost 50 percent in recent days.
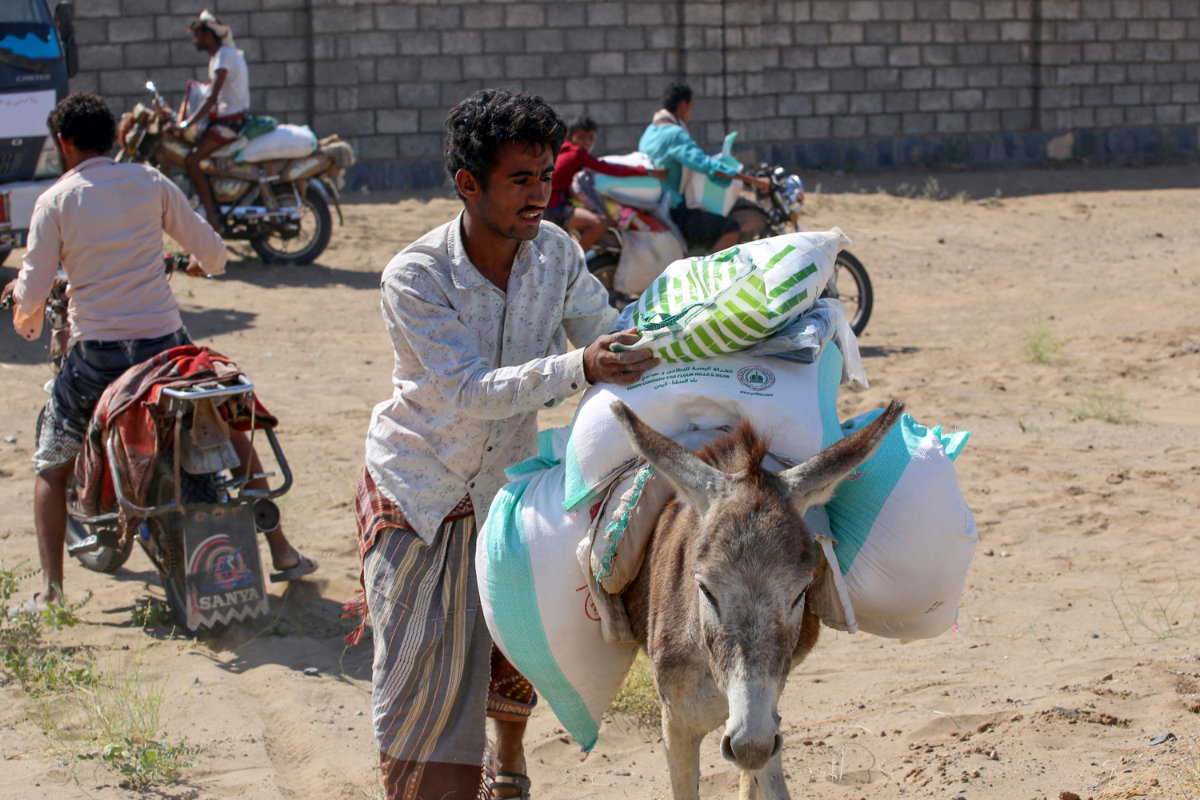

People displaced by conflict receive food aid to meet their basic needs at a camp in the Khokha district of Yemen's war-ravaged western province of Hodeidah, on Jan. 14, 2022. (Khaled Ziad / AFP)
Michael Tanchum, a non-resident scholar at the Middle East Institute, said: “Egypt already needs to find alternative suppliers. A further escalation that stops all Black Sea exports could also take Russian supplies off the market with catastrophic effect.”
Egypt imports the most wheat in the world and is Russia’s second-largest customer. It bought 3.5 million tons in mid-January, according to S&P Global. The Arab world’s most populous country has started to buy elsewhere, particularly from Romania, but 80 percent of its imports have come from Russia and Ukraine.
“With about four months of wheat reserves, Egypt can meet the challenge. But, to do so, Cairo will need to take immediate and decisive action, which can be made even more effective with the timely support of its American and European partners,” Tanchum added.

Egypt, the Arab world’s most populous country, buys 80 percent of its imports from Russia and Ukraine. (AFP file photo)
The war in Ukraine is also threatening to raise the cost of cooking oils in the MENA region and Turkey. A holdup of imports from Russia and Ukraine has sparked panic buying of sunflower oil in Turkey, despite government assurances concerning availability of basic items.
Ships carrying vegetable oil from Russia, which provides 55 percent of Turkey’s import needs, and Ukraine, which provides 15 percent, have been held up in the Sea of Azov. Concerns are likely to mount if the war affects this year’s harvest in Ukraine and if sanctions on Russia disrupt payments.
Amid the turmoil and chaos of the past two decades, the threat to food availability in the Middle East rarely reached alarming proportions. No matter how great the disruption, officials always found a way to keep the supply of staple foods flowing. The Ukraine crisis, which has plunged the world’s breadbasket into war, feels different in comparison. — with inputs from Reuters and AFP





































