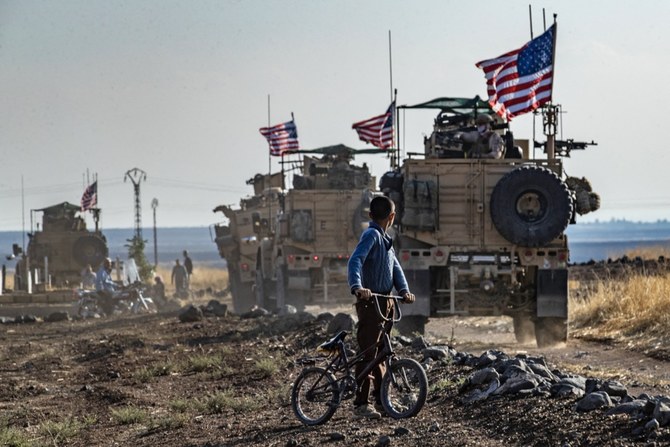
DUBAI: In October 2019, as Turkey massed its forces on the border with northeastern Syrian, threatening to invade and carve out a so-called safe zone, Kurdish communities just miles away turned to their powerful ally in Washington for support. The US military could keep the forces of their fellow NATO member at bay, the Kurds believed.
Five years of close security cooperation and the sacrifice of more than 11,000 lives in their joint fight against Daesh had convinced the Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces that the bond of trust that had grown between them and the Americans was unbreakable and that in the face of an even more formidable foe, their allies would surely have their back.
However, the Kurds were also prepared for the worst since a tweet by President Donald Trump and a White House video on Dec. 19, 2018, announcing the withdrawal of all American soldiers from Syria — save for a few hundred to guard oil fields near Deir ez-Zor.

“We never had the slightest intention of defending Ukraine, not the slightest,” said Anatol Lieven. (AFP)
As it turned out, by October 2019 Russian troops and Syrian forces had taken over at least three abandoned US camps in northern Syria. “Russian mercenaries splashed their good fortune over social media and took selfies in front of US equipment, while Russian reporters gave walking tours of the base,” Business Insider said in a report on Oct. 16.
Meanwhile, the Turks had launched bombing raids against the SDF in the name of “Operation Peace Spring.” The war effort against the global menace of Daesh — the US administration’s top priority just five years before — meant nothing to Trump. The SDF soldiers who had helped the anti-Daesh coalition win were summarily left twisting in the wind.
If the abandonment of the Kurds was a one-off, it could be dismissed as a blot on an otherwise honorable record. But recurrent American about-turns in recent years, in the Middle East and Europe, point more to a pattern than to a mistake. In Georgia, Iraq, Syria, Afghanistan and now Ukraine, peoples and governments that believed they could count on the superpower’s military support have all felt the crushing blow of its absence just when they needed it most.

Washington’s Gulf allies have learned the lesson the hard way. (AFP)
In a recent interview with the American Prospect magazine, Anatol Lieven, author of “Ukraine and Russia: A Fraternal Rivalry,” said: “We never had the slightest intention of defending Ukraine, not the slightest. Even though Britain and America and the NATO secretariat to the Bucharest Conference in 2008 came out for NATO membership for Ukraine and Georgia (the NATO HQ was completely behind it on American orders), no contingency plans were drawn up, not the most remote or contingent ones, for how NATO could defend Ukraine and Georgia. There was no intention of ever doing that at all.”
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
Lieven added: “Claiming that we were going to admit them to NATO: It goes beyond actual irresponsibility. In my view, this was deeply immoral, to make such a commitment that we had no intention of fulfilling.”
Last August, shocking scenes of planes careering down the runway of Kabul airport as desperate stowaways fell to their death from American military cargo planes’ wheel wells, came to be the defining image of a 20-year US occupation. Not far behind were scenes of Taliban fighters walking into Kabul as victors of a long war, their arch-foe having fled, and the national army raised by the US having folded almost overnight.

“There is no doubt that the Russian intervention in Ukraine is an accumulation of a series of Russian military interventions in Georgia in 2008,” said Ibrahim Hamidi. (AFP)
Two decades after promising to bring democracy and freedom to Afghanistan, the US had simply given up. First Trump, and then Joe Biden, had walked away from a clear moral obligation to a population that had made an enormous sacrifice in blood for America’s protracted “war on terror.” Nine months on, Afghanistan is a broken country, ruled by an unpopular Islamic fundamentalist group handed power practically on a platter by a nation that has lost the will to lead and the patience to keep fighting.
In the Middle East, where the US has trod with a heavy footprint since 9/11, there is little faith that a country suffering so much from political polarization itself has a coherent vision to offer.
Since 2000, the pendulum has swung between the missionary zeal of George W. Bush’s advisers and the cold-hearted realism of Barack Obama loyalists, and between the transactional mindset of Trump and the “Obama lite” image of Biden.

“The future of Europe and the EU looks much different today than it did just a week ago,” said Carl Bildt, Co-chair of European Council on Foreign Relations. (AFP)
At different times in the past two decades, Washington’s foreign policy priorities have been dictated either by human rights, commercial interests, democracy promotion or individual whims. Such a protean approach has taught even friends to be wary.
Washington’s Gulf allies have learned the lesson the hard way. The warm embrace of one administration as an essential regional security partner was replaced in 2020 by the aloofness of the next, compounded by rushed overtures to Iran.

The recognition of Iran as a malign actor and the threat posed by proliferating Iranian proxies in the region fell of the priority list almost overnight, while the Houthis were removed from the terror list, despite the group’s implication in the destabilization of the region’s poorest country, Yemen, and attacks on civilian facilities and population centers in Saudi Arabia and the UAE.
Commenting recently on Twitter on America’s Gulf partners’ neutrality on the Ukraine crisis, Hasan Alhasan, a research fellow at the International Institute for Strategic Studies, found “the subliminal message: this isn’t our war” similar to the “one consistently (sent) by the US to the Gulf states on Yemen and Iran over the past several years.”
Referring to the 2015 Iran nuclear deal, Alhasan added: “Iran has wreaked havoc in the region and has been locked in proxy war with Saudi/UAE. But the US, and especially the EU, were ready to normalize ties with Iran following JCPOA regardless.”
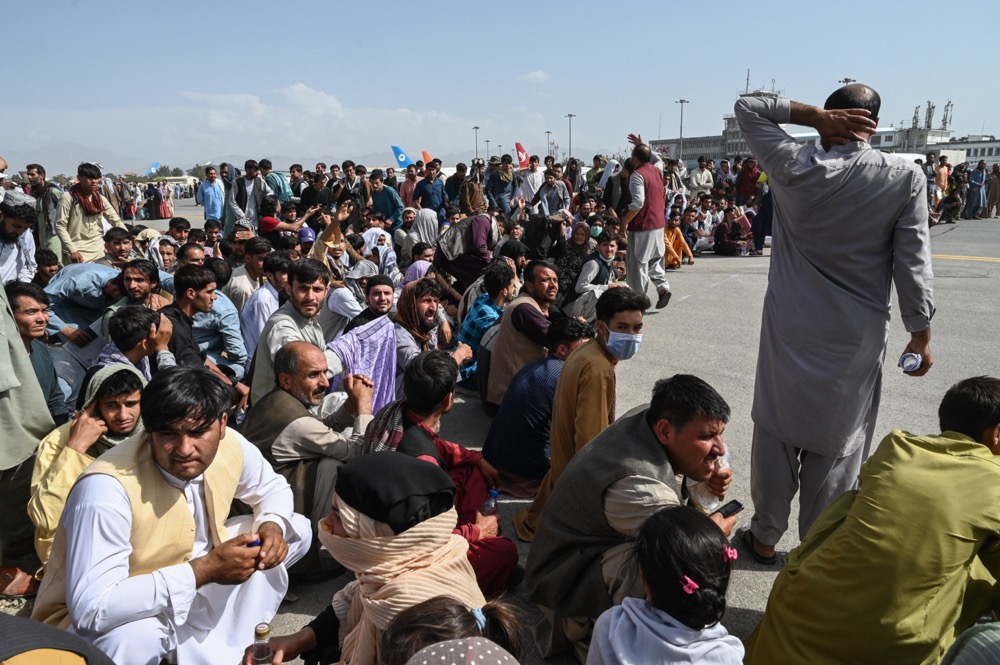

Two decades after promising to bring democracy and freedom to Afghanistan, the US had simply given up. (AFP)
More than two years on from Trump’s Syria pullout, the SDF, a mixed Kurdish-Arab military unit raised and funded under the Obama administration to lead the fight against Daesh, has not recovered militarily from the US betrayal. Kurds across the border in Iraq, who also took part in the global coalition’s campaign against Daesh, remain similarly wary.
The notion about the US being an all-weather partner and natural ally in whom Kurds of the Middle East could blindly trust during times of need proved especially fanciful during the Trump presidency.
Six years before the Syrian withdrawal, Obama made another decision that likely changed the course of the country’s civil war, while casting doubt on the ability or willingness of the West to demonstrate the courage of its stated convictions.
If any issue could stir Western leadership, the widespread use of chemical weapons on civilians would surely be it. But when Syrian President Bashar Assad gassed opposition forces as they approached the gates of Damascus, killing more than 1,300 on a late summer morning in 2013, the “red line” Obama had set as a trigger for intervention suddenly became a negotiation point.
Instead of standing with Syrian civilians, with his inaction Obama condemned them to another decade of misery, collective punishment and war crimes. Impunity became entrenched in Syria, and within a few years Russia would benefit from it most.

Washington’s foreign policy priorities have been dictated either by human rights, commercial interests, democracy promotion or individual whims. (AFP)
With the Assad regime in its pocket, America’s chief geopolitical adversary was able to establish a training ground in the lead-up to the annexation of Crimea in 2014, which, in hindsight, was a dress rehearsal of sorts for what was to come in February 2022 — the invasion of Ukraine.
“There is no doubt that the Russian intervention in Ukraine is an accumulation of a series of Russian military interventions in Georgia in 2008, Crimea in 2014 and Syria in 2015,” Ibrahim Hamidi, senior diplomatic editor for Syrian affairs at Asharq Al-Awsat newspaper, told the Associated Press news agency recently.
Putin “believes that America is regressing, China’s role is increasing, and Europe is divided and preoccupied with its internal concerns, so he decided to intervene.”