DUBAI: The Biden administration is considering acknowledging the genocide of ethnic Armenians by the Ottoman Empire, Ian Bremmer of GZero Media has reported in the lead-up to Armenian Genocide Remembrance Day, April 24.
In the event, Joe Biden would become the first US president to recognize the systematic killing of an estimated 1.5 million Armenians from 1915 onwards in modern-day Turkey as a “genocide,” a step already taken by the Senate and the House of Representatives in 2019.
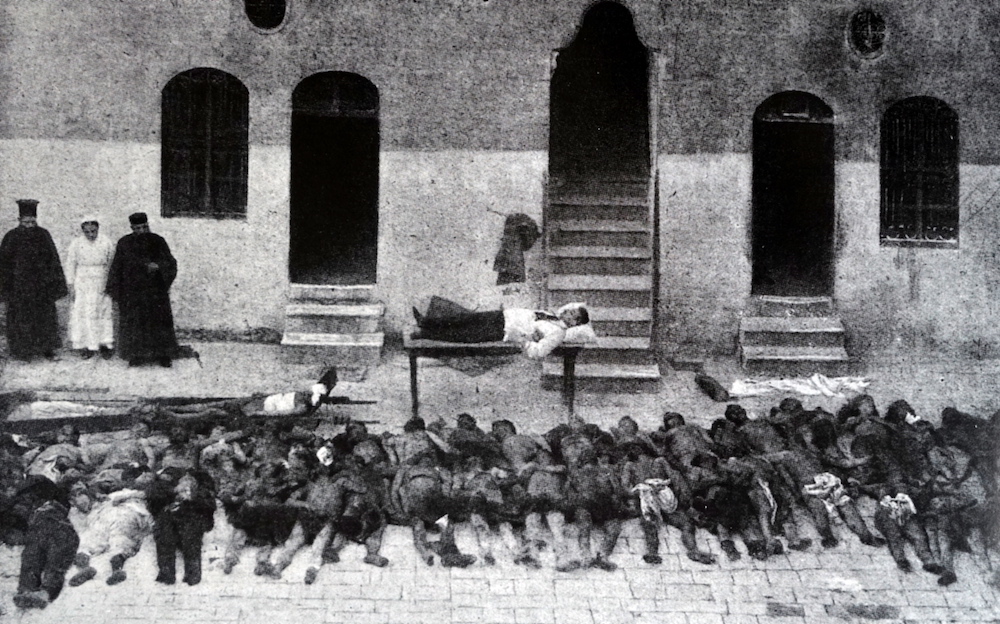

The atrocities started with the arrest of Armenian intellectuals in Constantinople in 1915 and continued with a centralized program of deportations, murder, pillage and rape until 1923. (AFP/Getty Images/File Photo)
The adoption of that measure by the two US chambers of Congress came at a time when Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan’s military intervention in northern Syria had strained already tense relations between his government and the US political establishment. This time around, in addition to continuing friction in US-Turkish relations, some 38 senators have sent a letter urging the president to recognize the genocide.
The atrocities started with the arrest of Armenian intellectuals in Constantinople in 1915 and continued with a centralized program of deportations, murder, pillage and rape until 1923. Ordinary Armenians were then driven from their homes and sent on death marches through the Mesopotamian desert without food or water.
Ottoman death squads massacred Armenians, with only 388,000 left in the empire by 1923 from 2 million in 1914. (Turkey estimates the total number of deaths to be 300,000.)
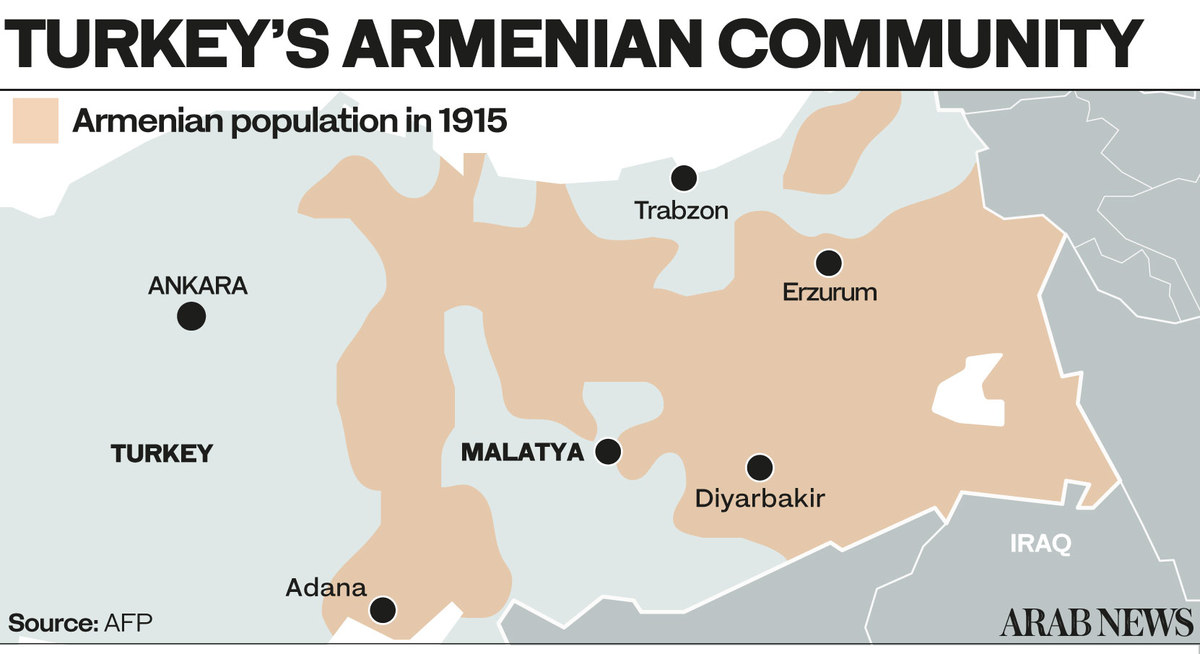
Many Armenians were deported to Syria and the Iraqi city of Mosul. Today descendants of the survivors are scattered across the world, with large diasporas in Russia, the US, France, Argentina and Lebanon.
Turkey admits that many Armenians living in the Ottoman Empire were killed in clashes with Ottoman forces during the First World War, but disputes the figures and denies that the killings were systematically orchestrated and constitute a genocide.
Getting access to vital Ottoman sources is a daunting challenge, while the language barrier makes access to Armenian sources hard for Ottomanists and comparativists alike.
Consequently, some scholars argue, Armenians have often been depicted as passive victims of violence, ignoring their active resistance during the genocide.
“This misrepresentation is due to a combination of political realities, methodological challenges, and the inaccessibility of crucial primary sources. The Turkish state’s denial of the Armenian genocide was a major hurdle,” Khatchig Mouradian, a lecturer in Columbia University’s Department of Middle Eastern, South Asian and African Studies, told the website Columbia News in a recent interview.
In a new book, Mouradian has challenged depictions of Armenians as passive victims of violence and mere objects of Western humanitarianism. “The Resistance Network” is a history of an underground network of humanitarians, missionaries and diplomats in Ottoman Syria who helped to save the lives of thousands during the Armenian genocide.
“I weave together the stories of hundreds of survivors and resisters as they pushed back against the genocidal machine in Aleppo, Raqqa, Deir ez-Zor, and in concentration camps stretching along the lower Euphrates,” Mouradian said. “In doing so, I place survivor accounts in conversation with — and sometimes in rebellion against — the scholarship and accepted wisdom on mass violence, humanitarianism and resistance.”
ARMENIAN GENOCIDE IN NUMBERS
* 2m Armenians living in Turkey in 1914, when genocide started.
* 1.5m Highest estimate of deaths, by massacre, starvation or exhaustion.
* 3,000 Years since Armenians made their home in the Caucasus.
* 30 Countries whose parliaments have recognized the genocide.
He said the Armenian case demonstrates how much is suppressed from the narrative when the actions and words of the targeted groups are relegated to the margins.
When historians use the term “Seferberlik” — the Ottoman word for “mobilization” — it is often assumed they are discussing the Armenian genocide. But it is also used to refer to another smaller but significant episode of mass displacement that occurred around the same time in what is today Saudi Arabia.
“Seferberlik: A century on from the Ottoman crime in Madinah” — by Saudi author Mohammad Al-Saeed — tells the story of the deportation of the holy city’s population by Ottoman General Fakhri Pasha.
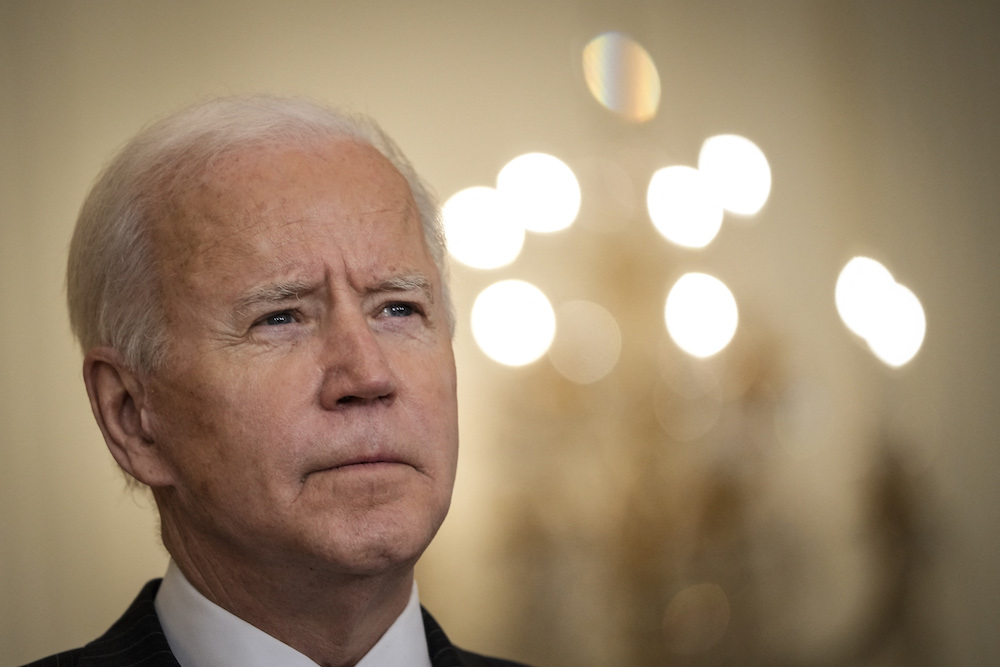

Joe Biden looks set to become the first US president to recognize the systematic killing of an estimated 1.5 million Armenians from 1915 onwards. (Getty Images via AFP)
History books tell of Fakhri Pasha’s “heroic defense” of the city in the 1918 Siege of Madinah, fending off repeated attacks by the British-backed Arab fighters of Hussein bin Ali, the Sharif of Makkah. However, the books prefer to gloss over what happened in 1915, prior to the siege, when Fakhri Pasha forced Madinah’s population onto trains and sent them north into present-day Syria, Turkey, the Balkans and the Caucasus.
“The Seferberlik crime was an attempt to transform Madinah into a military outpost,” Al-Saeed told Arab News in a recent interview. “The Turks tried to separate the city from its Arab surroundings and annex it to the Ottoman Empire to justify ruling what remained of the Arab world.”
He said history should not forget what happened in Madinah, particularly since the few historical sources that documented the events are in the Ottoman, English and French archives.
READ MORE
Arab News Spotlight: Why the Armenian Genocide won’t be forgotten. Click here to read the full article.

“Moreover, the sources of information are very limited and the grandchildren of those who were in Madinah at the time do not have many documents. A lot of the city’s inhabitants were displaced. Many of them did not return,” Al-Saeed said.
Speaking to Arab News in 2019 on the Armenians’ displacement experience, Joseph Kechichian, senior fellow at the King Faisal Center for Research and Islamic Studies in Riyadh, said: “My own paternal grandmother was among the victims. Imagine how growing up without a grandmother — and in my orphaned father’s case, a mother — affects you.
“We never kissed her hand, not even once. She was always missed, and we spoke about her all the time. My late father had teary eyes each and every time he thought of his mother.”
Every Armenian family has similar stories, said Kechichian. “We pray for the souls of those lost, and we beseech the Almighty to grant them eternal rest,” he added.
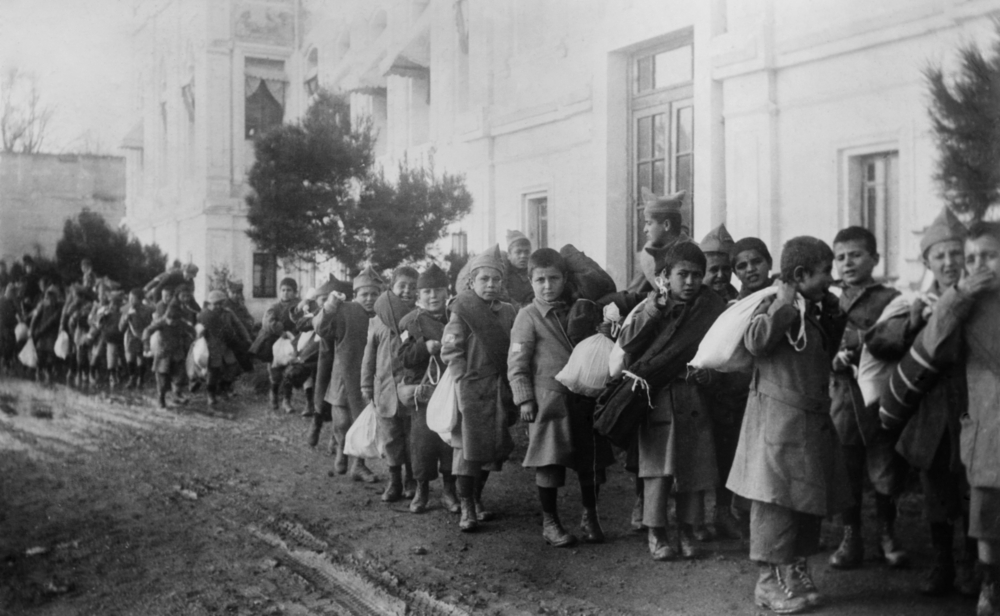

Armenian orphans being deported from Turkey in around 1920. (Shutterstock/File Photo)
According to genocide scholars, denial is the final stage of genocide. Levon Avedanian, coordinator of the Armenian National Committee of Lebanon (ANCL) and professor at Haigazian University in Beirut, said that for Armenians, the denial of the Armenian genocide by Turkey is a continuation of the genocidal policies.
“In that sense, recognition by Turkey and by members of the international community is an essential step on the long path of restoring justice, which would inevitably include, in addition to recognition, reparations and restitution,” he said.
As a Democratic presidential candidate, Biden tweeted on April 24 last year: “If elected, I pledge to support a resolution recognizing the Armenian Genocide and will make universal human rights a top priority.”
In his “quick take” of March 22 on the possibility of Biden making good on his campaign promise next month, GZero’s Bremmer summed up the situation this way: “A lot of things going wrong for Turkey right now. They just pulled their country out of the Istanbul Conventions, European agreement that meant to protect women. And (Erdogan) also just sacked his new central bank governor. … The economy is not doing well. … he’s cracking down on the pro-Kurdish People’s Democratic Party, the HDP. … But the big news, is that Erdogan is about to face another diplomatic challenge.”































