DUBAI: Clad in a neat white kurta, Kailash Satyarthi comes across as an unassuming man. But when the Nobel Peace Prize winner starts to speak, it is impossible not to be gripped by his story of a four-decade struggle against child labor and slavery.
Earlier this month, the 65-year-old Satyarthi was in the UAE for a private screening of his documentary, “The Price of Free,” winner of the 2018 US Documentary Grand Jury Prize at the Sundance Film Festival.
The film traced his work fighting for children’s rights, but now he has a new aim: A campaign for international laws to protect the young from online abuse and exploitation.
“The way the Internet and smartphones have penetrated our lives — regardless of whether you are rich or poor — is unbelievable,” he said. “This digital explosion has also led to many serious problems. Online child abuse is certainly one of them.”
 Satyarthi has written to political leaders across the world, calling for a new convention on the issue. “Given that online crimes transcend borders, extra-territorial jurisdiction for the proposed law is absolutely essential. We need a dedicated, toll-free international helpline for reporting cases related to online child sexual abuse, under the supervision of the International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol) and other relevant agencies,” he said.
Satyarthi has written to political leaders across the world, calling for a new convention on the issue. “Given that online crimes transcend borders, extra-territorial jurisdiction for the proposed law is absolutely essential. We need a dedicated, toll-free international helpline for reporting cases related to online child sexual abuse, under the supervision of the International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol) and other relevant agencies,” he said.
After graduating as an engineer, Satyarthi started campaigning for child rights where he lived, in a small town near Bhopal in central India. “In 1981, a poor Muslim family knocked on my door. They needed help to find their 15-year-old daughter, who was enslaved,” Satyarthi recalled.
With the help of local villagers and his friends, he worked to have her freed. The family and the girl are still in touch with him: “They are part of my family now.”
That was where he began. Supported by a group of fellow activists, he would raid sites where children were forced to work and free them, sometimes with the support of the authorities, but often with only the help of local villagers.
Battling an unresponsive system, he survived multiple attacks, and now travels around the world, throwing his weight behind efforts to free children from forced labor and slavery. In India alone, Satyarthi and his foundation have been credited with freeing 87,000 children.
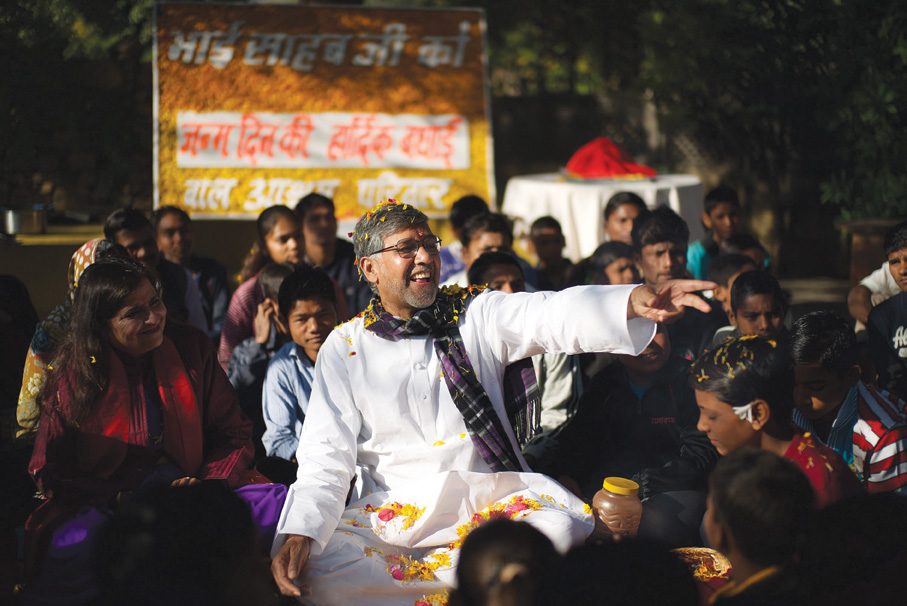

Children’s campaigner Kailash Satyarthi with supporters of his advocacy. (AFP)
In 1996, he began a campaign for an international law against child labor. This led to a “Global March Against Child Labor” in 1998, in which he walked 80,000 km across 103 countries. As a result, in 1999, the International Labour Organization (ILO) adopted Convention 182: Prohibition and Immediate Action for the Elimination of the Worst Forms of Child Labor.
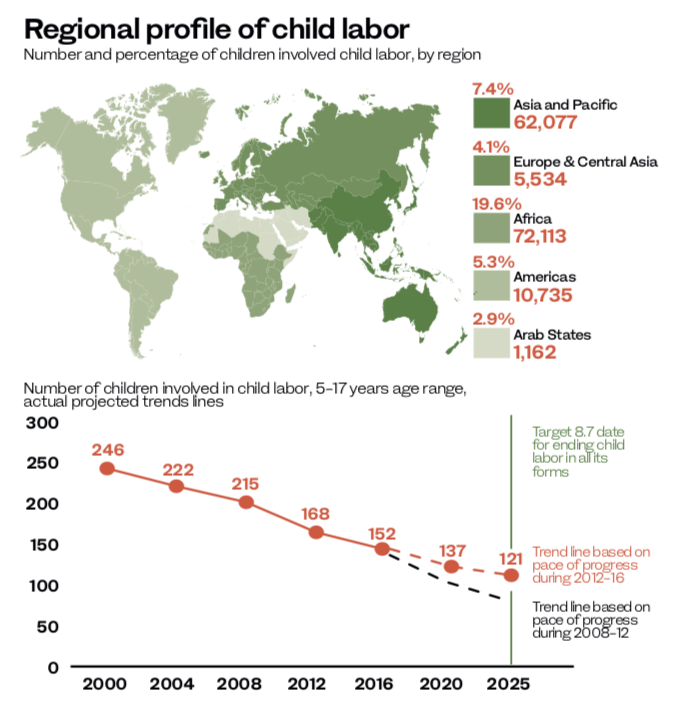
Yet, the struggle continues. According to the latest ILO estimates, 152 million children are involved in child labor, including slavery, trafficking, debt bondage and other forms of work, and forced recruitment for armed conflict, prostitution, pornography and other illicit activities.
Even in the Arab world, 1.2 million children are working as child laborers and 616,000 are involved in hazardous work. Despite being the lowest figure of any region in the world, it still means about 3 percent of children are involved in child labor.
Africa ranks highest, both in the percentage of children in child labor — around 20 percent — and the absolute number of children — 72 million. Asia and the Pacific ranks second highest on both these measures, with 7 percent of all children and 62 million in absolute terms.
Globally, 64 million girls and 88 million boys are still in child labor, accounting for almost 10 percent of all children worldwide. Making things worse, almost half of all them are in hazardous work that threatens their health and safety.
For Satyarthi, though, it is not all bad news. In fact, he has reason to believe that his struggle is bearing fruit. “It has been a long journey, but a fulfilling one. In the year 2000, there were 260 million children working. And in 2018, the number has come down to 152 million,” he said.
According to Satyarthi, child labor is linked to poverty and illiteracy. “If we need to fight against child labor, we need to work on illiteracy and poverty eradication,” he said.
This is precisely what his organization, the Children’s Foundation, has been doing in 144 countries for more than 20 years. The fight has not been easy anywhere, but he found the sub-Saharan African region the most difficult. “Weak governance, apathy and corruption,” he said. “Rehabilitation of these children has always been an issue because of a lack of resources and facilities.”
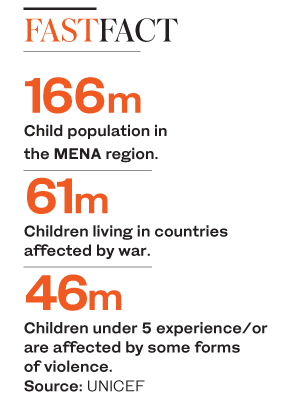
Satyarthi’s dedication to the cause also brought him to the Middle East, where his primary focus has been on protecting child refugees. Of the 166 million children living in the region, 61 million are living in countries affected by war. According to Satyarthi, governments around the world, especially in Europe, are unnecessarily reluctant to host refugees, especially children.
“Please do not assume that you are doing any favors to these (refugees). They are not going to take anything from you. These poor souls are victims of circumstance. It is the responsibility of the world to take care of them,” he said.
He recalls a meeting with a 10-year-old Syrian boy in a refugee camp in Germany. The youngster — who had lost both his arms and had no parents — somehow reached Germany with the help of family friends.
“Despite what he had been through, the child looked confident and positive. He told me he is not going to live in Germany forever. He wanted to go home to Syria. He wanted to become an engineer and build new houses for his countrymen who have lost theirs.”
Satyarthi also had words of appreciation for Arab governments and their efforts in taking care of the refugees. “Arab governments are sensitive about the issue. They are taking care of Arab refugee children very well. They are spending money to make sure they remain safe.”
He also took the opportunity to urge compassionate leaders, governments and businesses in the Gulf to extend their fullest support to refugee children and their communities “so that they are protected, sheltered and nurtured for a promising tomorrow.
“Otherwise an entire budding generation will be wiped out,” he said.
Satyarthi has always believed that refugees are a global responsibility and much more needs to be done to safeguard their interests. Moreover, several layers of support need to be established to improve things.
“Though the problem is regional, it should not be treated as so. It is a global responsibility,” he said.
“Every border should be open. Every treasury should be free and every heart should be open for children.”
“The Price of Free” is available for screening on YouTube.
For more information, visit https://priceoffree.com