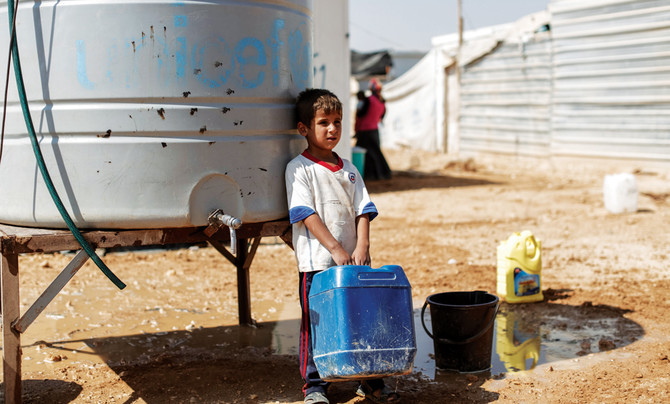
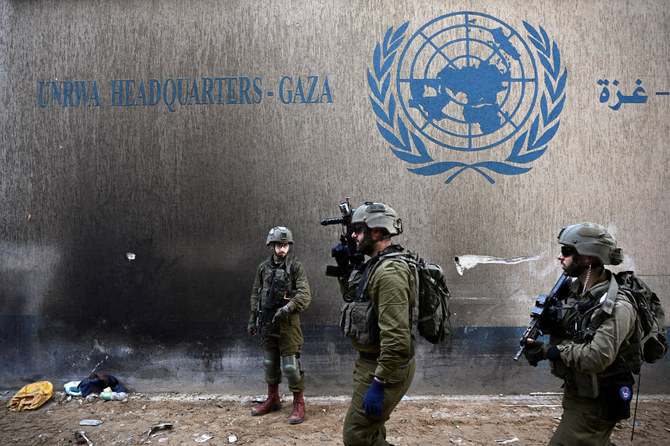
DUBAI: With only two percent of the Arab region covered by wetlands, and 94 percent of those vulnerable to climate change, water will play a crucial role in the future functioning of the region’s ecosystems.
Regional and global decision-makers, scientists and experts discussed the challenges and potential solutions at this year’s World Water Week in Stockholm, Sweden.
Hosted and organized by the Stockholm International Water Institute (SIWI), the 23rd edition, which started on Sunday, focuses on water, ecosystems and human development.
“This has implications for rural communities, livestock, migratory birds and even wastewater management in peri-urban areas that use wetlands to support nature-based solutions to wastewater management,” said Carol Cherfane, chief of water resources in sustainable development and productivity at the UN Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia. “Climate change exacerbates water scarcity and in turn affects water security in the region. This is demonstrated by the impact that climate change is having on water resources, ecosystems and agriculture across the region.”
Cherfane, who attended the event, said water is a fundamental aspect of development, peace and security in the Arab region. “New solutions are needed to ensure access to water in areas facing conflict, and particularly for women, children and vulnerable groups.”
For Monika Weber-Fahr, global water partnership executive secretary and speaker at the event, the Middle East is not unique when it comes to water management conflicts. “Water scarcity, one of the main reasons for water conflict — but not the only one — is common in other parts of the world, and increasing in many places,” she said. “Some parts of the Middle East have particularly severe water scarcity. Obviously, if a resource is scarce, there is bound to be conflict. Fortunately, people recognize that water is an essential resource and will do their best to figure out ways to share its benefits.”
Global Water Partnership has long advocated for integrated water resources management, which is about public participation and cross-sectoral cooperation. “To solve water problems, you need to have everyone around the table,” she said. “Too often, decisions are made that are fragmented or taken without listening to the users. In addition, there are options for helping to solve water scarcity problems such as water harvesting and the reuse of wastewater.”
Weber-Fahr said the situation is critical and one reason why, on Aug. 30 and 31, GWP is convening, with other organizations, a meeting of “Blue Peace in the Middle East” in Stockholm. “There are regional representatives from six countries and the purpose is to look at how water can be used more efficiently, especially in agriculture. ”
Experts discussed water diplomacy, water utilities’ response in conflict conditions and water management in conflict. “We are already living in a water-scarce region and getting access to the right quantity and quality of water is, most of the time, very challenging,” said Dr. Khalil Ammar, principal scientist in hydrogeology and water resources management at the International Center for Biosaline Agriculture in Dubai. “Some countries are doing much better than others, but when you add to this problem more unrest, it will make it a lot more difficult. Migration affects access to water resources.”
He gave the example of Jordan, which hosts more than 650,000 Syrian refugees, according to the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs. The Jordanian government estimates there are 1.4 million Syrians in the country, including those who have not registered as refugees. “The country already has a very limited amount of water and this has added a big burden in terms of finding the right quantities of water,” Dr. Ammar said. “This is because policy-makers decided to prioritize water to the industry and for municipal purposes (rather) than for agriculture — the percentage for agriculture is now much less compared to other regional countries, including the UAE, at about 52 percent.”
In times of conflict, national priorities change. “Conflict adds a lot to the severity of the water problem,” he added. “There are difficulties in accessing water for residents and it adds more burden on the budget and investment in infrastructure. In unstable areas, the cost of implementing these will be much higher and reaching the right people will also be very difficult.”
He called for improved management of water allocation systems and increased investment in infrastructure. “In Iraq, the priority went to war rather than human needs,” he said. “The quality of the water deteriorated a lot and it’s really become a regional problem, engulfing Lebanon as well as Turkey.”
Two billion people depend on groundwater sourced from transboundary aquifer systems. There are 276 river basins crossing the boundaries of two or more countries, and 40 percent of the world’s population rely on these rivers as a primary source of freshwater. But as much as 60 percent of the world’s international river basins lack any cooperative management framework.
“Water is becoming an important issue because of its scarcity and our location in an arid area where the amount of input and rainfall is less than what is pumped from many water resources,” said Dr. Ahmed Murad, dean of the college of science at United Arab Emirates University. “We also have a high rate of evaporation, exceeding the limit of recharge to aquifers so, in general, that causes an imbalance between the recharge and discharge from major aquifers.”
Population growth is also an obstacle as it adds stress to natural water resources. The world’s urban population increased to 54 percent of the world population in 2014, a figure that is expected to grow to 70 percent by 2050 and, according to Dr. Murad, could affect future development. “We need to look at innovative approaches to harvest the water available. A good model is the UAE with (cloud seeding) initiatives. We also need to change our social behavior as it plays a major role — any conflict additionally affects people reaching water resources.”
With annual rates of less than 250 millimeters of rainfall in the Middle East, ecosystems are fragile and under stress. “All ecosystems depend on water for them to continue their function, hence destroying ecosystems means losing their function services to us and therefore impacting our well-being,” said Dr. Waleed Zubari, professor in water resources management at the Arabian Gulf University in Bahrain. “We will need to manage our water resources in a way that does not deprive ecosystems of their water. Although the GCC has been providing commendable rates for drinking water and sanitation services to its population, some countries still face many challenges, the most important of which is increasing water scarcity with time.”
Such countries are also experiencing accelerated socio-economic development, which requires large quantities of water that are beyond the capacity of their natural water resources. “Therefore, the GCC has to rely on non-traditional water resources, represented mainly by desalination, to meet the municipal and industrial sectors’ water requirement, and reuse of treated wastewater to supplement groundwater in the agricultural sector,” he said. “Rapid population and urbanization growth are challenges as well as high per capita consumption patterns.”
About 40 percent of the Arab population is already living in conditions of absolute water scarcity. From 2005 to 2015, annual per capita freshwater availability in the region dropped by about 20 percent, from about 990m3 to 800 m3. “It is even far less in some countries,” said Dr. Redouane Choukr-Allah, head of salinity and plant nutrition laboratory at the Institut Agronomique et Veterinaire Hassan II in Morocco. “Half of total renewable water resources in the Arab region originates from outside its borders in the absence of legal agreements to organize water-sharing. Overexploitation and pollution of water resources are reasons for low water quantity and quality as well as ecosystem degradation.”
He said that the effects of climate change worsen the situation. By 2030, those effects are expected to reduce renewable water resources by another 20 percent through declining precipitation, rising temperature and sea levels as well as expanding seawater intrusion into coastal aquifers. “The majority (84 percent) of water resources in the region are being used for agriculture while the municipal and the industrial sectors consume about 9 and 7 percent of the total water use respectively. Being an important vector for socio-economic development, there is a need for efficient and sustainable water management to ensure that the water sector can continue to serve the region’s development needs.”
With World Water Week bringing together scientists and practitioners to raise awareness about the latest knowledge and innovations in areas most affected by water scarcity, sustainable development will require water-smart societies. “We don’t have an infinite resource lying around for us to use,” said William Shintani, managing partner at MBLM in Dubai, which promotes the consumption of local drinking water. “We’ve learnt the hard way in the region to take care of them — the better we manage them, the better it will be for future generations. There’s no way any civilization will flourish or any region will witness economic progress without water.”
He said that education was a key component of that future success. “Governments are helping to implement a lot of programs to teach younger generations about their resources and the ecosystem.”
Improved infrastructure across the board will also be needed.
“There should be far better infrastructure planning when you’re building a city,” said Rishi Kohli, managing partner and co-founder of Waterwise in the UAE. “Nowadays, governments are becoming more aware of water management and those sorts of initiatives are slowly creeping into regions and residential communities. If you just let things be and not control and manage it, then you’ll have huge ramifications in the future for our children. We are just touching the surface.”