LONDON: The WHO Foundation was set up in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic to marshal new resources from philanthropists, foundations, businesses, and individuals to support the World Health Organization’s mission.
Both WHO, which is a specialized agency of the UN, and the WHO Foundation are based in Geneva but the latter is a non-profit, grant-making body that is legally independent from WHO.
Anil Soni joined as CEO with a 20-year track record of improving healthcare in poorer countries and a goal to raise $1 billion. He told Arab News, in a written interview, how his foundation supports and complements WHO’s efforts while respecting its intergovernmental nature.

WHO Foundation CEO Anil Soni. (Supplied)
Arab News: Can you describe how the WHO Foundation arranges support from donors and how the money is spent by WHO?
Anil Soni: The WHO Foundation’s purpose is to be a bridge between the lifesaving and vital work of WHO and the various communities that can help power that work through their engagement, partnership and of course, generosity.
We are raising resources from multiple partners from the private sector and beyond to help WHO deliver lifesaving medicines and supplies to people in need.
World challenges such as the Turkiye-Syria earthquakes, the food crisis in the Sahel and the Horn of Africa and the conflict in Ukraine are great examples of where we are facing crises that affect all of us and have to come together.
Such adversities cannot be tackled by any single sector alone. WHO is part of several international organizations of the United Nations, but the UN and the governments are not enough. We have to make sure we are collaborating with individuals and businesses too.

Photo taken on June 10, 2012 shows Dr. Omar Saleh [2-L], the emergency coordinator for WHO in Somalia, attending to a young patient at a hospital in the Hudur region. (AFP file)
All contributions matter, even small ones, as these add up to enabling life-changing initiatives. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, we had a campaign called “Go Give One.” Five dollars bought a vaccine, the same amount of money that could go into buying a cup of coffee. Businesses and philanthropists were donating millions of dollars, and that’s important, but every single contribution counts.
In terms of how we mobilize the money, we do it in several ways. We are brokering catalytic, transformative ways of engaging with philanthropists and businesses looking for opportunities to contribute to change and be part of the solution.
In the case of the earthquakes that affected millions and led to more than 50,000 life losses (the biggest death toll in over a decade since the Haiti earthquake), WHO continues to procure and quickly deliver lifesaving tools in Turkiye and Syria.
One of our closest partners is Spotify. Spotify created an opportunity for its listeners to contribute to the relief efforts in Turkiye and Syria by helping direct individuals (Spotify users) to our donation webpage.
Each donation directly supports relief efforts for those affected, including mental health services, physical rehabilitation, medicines, and other tools or commodities needed to reduce the risk or respond to communicable diseases from poor access to hygiene, clean water, and health services.
Q: Aid agencies have been criticized over the perception of unfair aid distribution and assistance in earthquake-hit areas, particularly in relation to Syria and its different areas of control. How can aid in this complicated context be made more equitable?
A: Often, people at risk and in need are in environments that are the subject of intense political debate or literally in the crossfire of conflict. This is one of the reasons why WHO’s work is so important, as it operates everywhere. It is a UN agency that is itself a collaboration between member states. Hence, all the world’s governments participate in the operations and governance of WHO.
INNUMBERS
501,000 People who died from tuberculosis in Africa in 2021.
43,000 Excess deaths caused by hunger and poor health in Somalia in 2022.
57,300 Deaths in Turkiye and Syria caused by Feb. 6 earthquakes.
Furthermore, WHO’s emergency teams are in all regions of the world, so they continue to operate in Syria through years of conflict and are one of the few that have done so. It is crucial not to be biased against people’s needs because of the nature of a political situation or conflict. Quite the opposite, this is about healthcare, delivering medical services, and doctors whose job is not to deal with politics but to ensure people in need receive adequate healthcare.
I was really inspired by Dr. Tedros (Adhanom Ghebreyesus), the head of WHO, who visited Syria last month. He was the first UN principal to enter northwest Syria in over a decade because of the conflict. In the first hours after the earthquakes, WHO distributed 183 metric tons of supplies to more than 200 health facilities inside northwest Syria from partner warehouses in Azaz and Idlib.
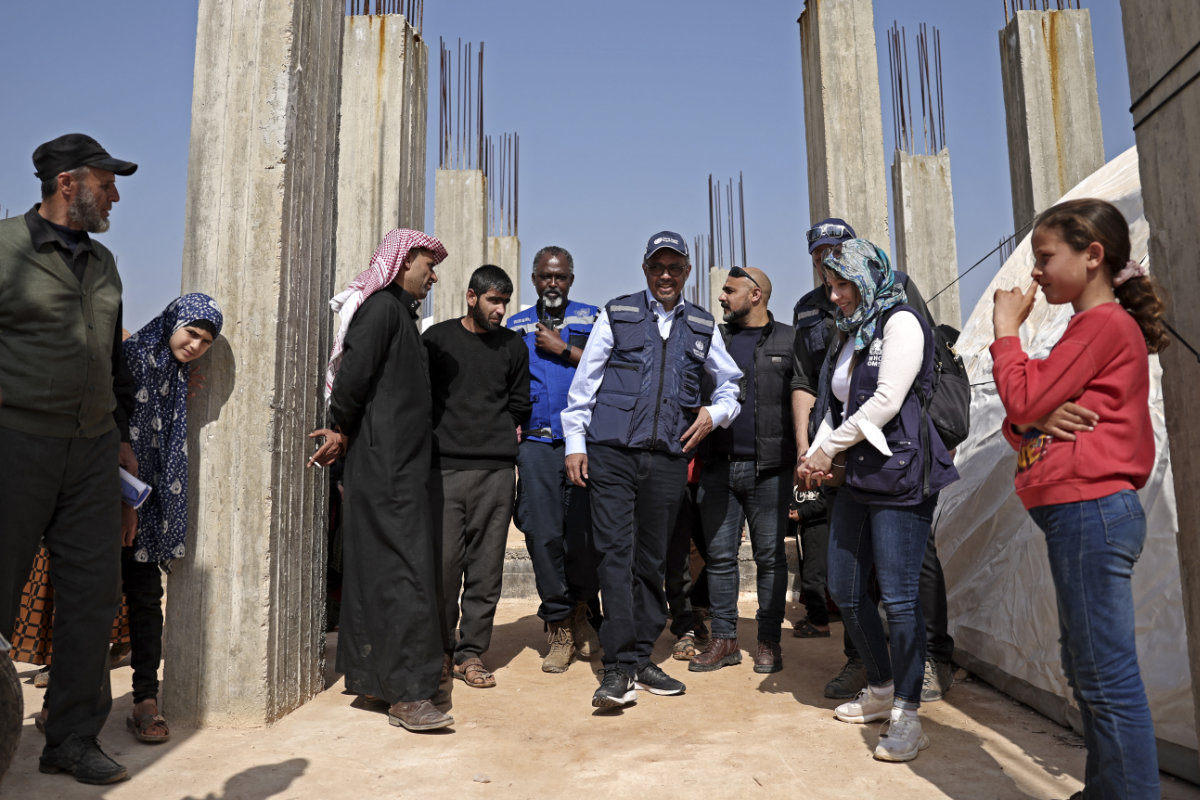

World Health Organization chief Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus (C) visits a shelter for people displaced by the disaster in Kafr Lusin near the Turkish border on March 1, 2023, during his first ever visit to rebel-held areas of war-ravaged Syria. (AFP)
Following this, WHO delivered 297 metric tons of emergency supplies and essential medicines to earthquake-affected areas of the country, allowing 3,705,000 treatments, including ones for trauma management, diabetes, and pneumonia.
Q: What are the main healthcare challenges facing the Middle East and North Africa region? How can mobilizing additional funding for WHO address these challenges? Can this go beyond monetary assistance to address the structural issues behind health inequality?
A: That’s the aspiration because otherwise, we will continue to face these emergencies and inequitable needs. The MENA region is striking at the moment because it is home to a number of simultaneous humanitarian and health crises that need both immediate assistance and long-term solutions.
Events such as the earthquakes in Turkiye and Syria, the conflict in Syria and the cholera outbreaks in Lebanon and Syria are acute and products of climate change or long-term dynamics that require sustained response and commitment.
The region now more than ever is uniquely positioned to support with its burgeoning economic prosperity among residents and the public and private sectors. It is vital to raise the necessary resources and awareness of how every single contribution plays a huge role in tackling humanitarian crises, which is what we do at the WHO Foundation.
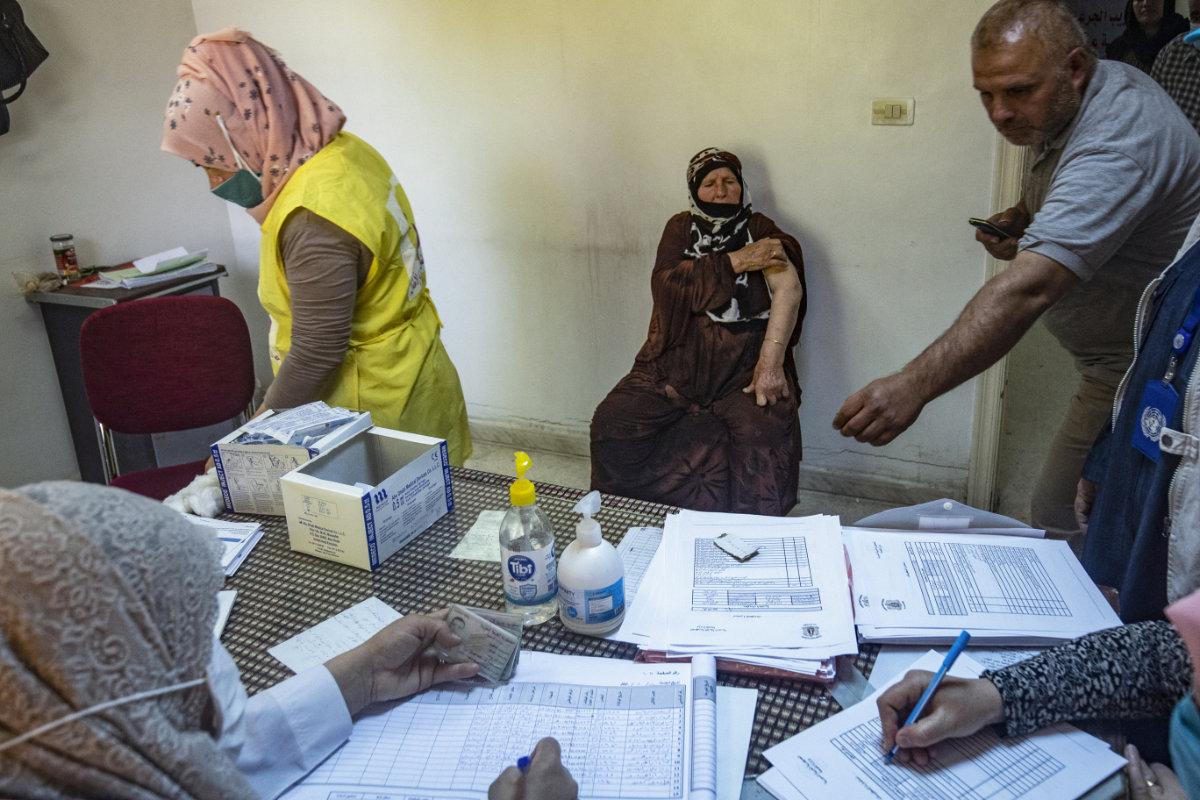
A Syrian medic administers COVID-19 vaccine provided by the WHO and UNICEF to people in Syria's northeastern city of Qamishli on May 24, 2021. (AFP)
But equally important is the need to address the structural issues and the systemic reasons behind inequalities and fully leverage the resources of some of our partners. For example, we’re not just looking to our partners as a source of capital. We are also looking into how they can help us mobilize humanitarian efforts through their platform, talent, ability and own supplies.
I mentioned Spotify earlier. They helped us engage millions of listeners to gather resources to build up local health systems and become better prepared for emergency response.
So, part of what we’re trying to do in terms of raising those resources and brokering these partnerships is not just responding in the moment of an emergency but also ensuring that the underlying health systems are being built up, that there are community healthcare workers and adequate supplies.
We think about long-term financing and building systems strong enough to allow us to be agile in our response to an emergency or even help predict future crises (that is, potential disease outbreaks).
Q: How is the WHO Foundation helping to improve global preparedness? Does this apply merely to COVID-19 and readiness for future pandemics or does it include other emerging health threats (environmental, nutritional, etc.)? How can states like Saudi Arabia prepare?
A: WHO and the WHO Foundation work collaboratively and proactively to improve preparedness. For example, we are setting up emergency hubs in Kenya, Senegal, and South Africa to bolster health security across the African continent. This helps ensure lifesaving medical supplies and equipment are shipped within 24-48 hours of the declaration of an emergency, reducing deployment time by up to 60 days.

WHO Foundation CEO Anil Soni in Kenya. (Supplied).
These regional emergency hubs work closely and cooperatively with governments for a joint emergency response, prepositioning of medical supplies and equipment, training facilities, and infectious diseases monitoring. But these emergency hubs are not limited to tending to diseases. They also help boost living quality, such as ensuring a continued supply of clean water to avoid risks of waterborne diseases like cholera.
WHO is always looking ahead, whether that’s analyzing trends in climate change or forecasting geopolitical outcomes, to anticipate better where our support will be most needed. We also work with governments and health leaders to help them navigate health crises their nation may have yet to experience.
Regarding Saudi Arabia, the vision and generosity of the Kingdom and its close collaboration with businesses and its people are very well-suited to this. As I understand it, particularly in the context of Vision 2030, Saudi Arabia is addressing how it can ensure that they recognize the interconnectedness between our well-being, the well-being of others, and the well-being of our neighbors. There’s a term in South Africa called “Ubuntu,” which means “I am because you are.”
It essentially recognizes interconnectedness and that the only way I will prosper is if I’m making sure that I’m being thoughtful about your needs because we depend on each other. I think this resonates with Saudi Arabia’s leadership role in the region and that supporting countries and communities inside and outside the Kingdom’s borders is essential to the welfare of the people in Saudi Arabia itself.
Q: What is your opinion of Saudi Vision 2030’s Health Sector Transformation Program? Do you believe its focus on equitable and accessible health care coincides with the WHO Foundation’s own mission and values?
A: Similarly to Saudi Arabia’s Health Sector Transformation Program, the WHO Foundation believes in equitable and accessible healthcare. To speak more broadly in terms of the Vision 2030, there’s also a focus on nonprofit efforts and a culture of strategic philanthropy.
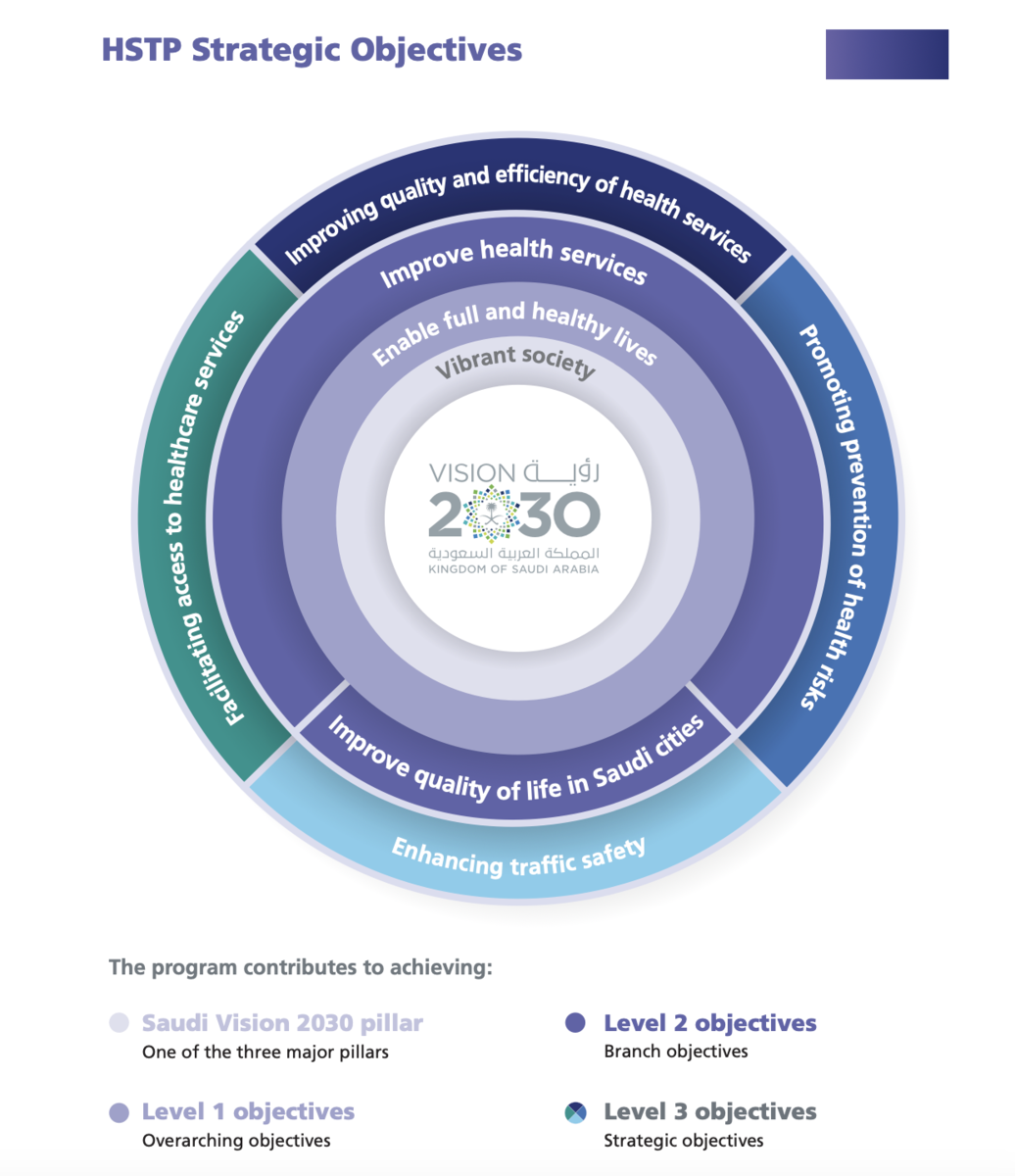
Infographic courtesy of Saudi Arabia's Vision2030 site
Even though there’s the government’s leadership, the rest of the nation is encouraged to contribute, including businesses and individuals, to addressing national challenges and fostering development. This idea of everyone playing a role in achieving goals is consistent with our mission at the WHO Foundation.
We’ve had to react to so much these last years, such as a pandemic that much of the world didn’t predict, the effects of climate change even though it’s been brewing over time, and natural disasters that have periodicity and history.
If we look back, earthquakes and tsunamis have caused so much damage over the decades, and the question is, are we preparing for such catastrophic events? If all we’re doing is reacting and not preparing, the effects will be greater, and the loss will be unnecessary.
I say all of that because, when a government like Saudi Arabia works backward all the way from 2030, proactively and not just reactively, it sets an important lesson for all of us and demonstrates how much progress we could make by simply being prepared.
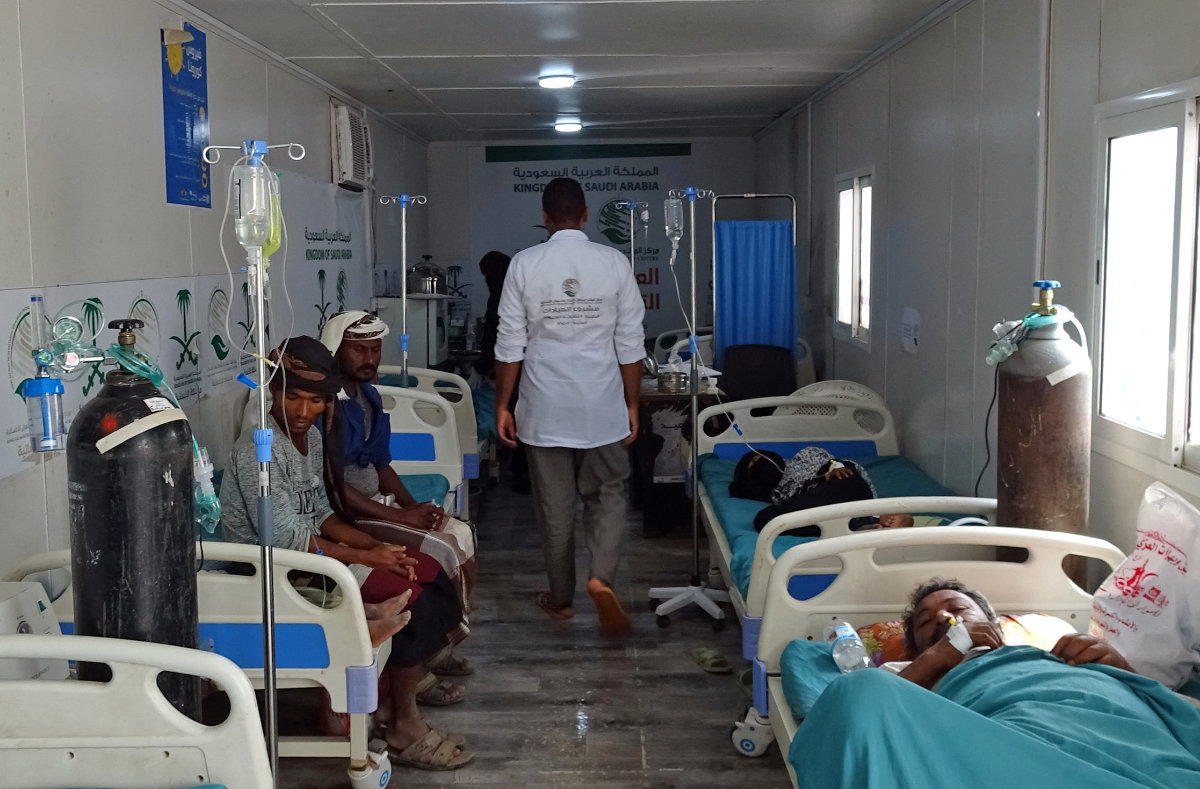
Displaced Yemenis receive medical treatment at a health clinic run by Saudi Arabia's KSrelief in Yemen's war-ravaged western province of Hodeida, on February 24, 2021. (AFP)
Q: What is the WHO Foundation’s assessment of Saudi Arabia’s role in supporting nations in the wider region, including the medical interventions of KSrelief? Does the Kingdom have a greater role to play in future humanitarian and disaster responses?
A: KSrelief is an incredible model, and we’re learning a lot from the existing collaboration between KSrelief, WHO and other international humanitarian partners. The generosity of KSrelief has been tremendous, but it’s not just about the number of dollars; they’re also thoughtful about the quality of aid and the policy frameworks necessary to ensure the positive impact intended. We want to replicate and build from this type of partnership and engagement.
Q: In what ways does the WHO Foundation want to mobilize greater private capital and public-private partnerships to advance the mission of WHO in Saudi Arabia and the wider region?
A: A part of what we are trying to do at the WHO Foundation is help stakeholders in Saudi and other countries in the region understand the critical role WHO plays. Though it was prominent throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, WHO is not just about responding to the pandemic; it responds to various emergencies; it’s operating in settings other agencies are not; it’s thinking and preparing for future emergencies.
Last month, WHO released its Global Health Emergency Appeals, enhancing preparedness and response to 54 ongoing health emergencies. And, of course, there’s all the normative work of WHO, the degree to which it acts as the world’s FDA, CDC, and NIH.

Yemeni children receive treatment at a hospital in the capital Sanaa on October 11, 2016 during a cholera outbreak confirmed by the World Heath Organization. (AFP)
We hope that by raising awareness and amplifying the understanding of WHO and its initiatives, we can engage the tremendous generosity of the region and mobilize regional stakeholders to help WHO achieve its humanitarian goals.
Q: Philanthropy is a key tenet of Islam. What role can zakat play in the WHO Foundation’s fundraising work in the region?
A: I’ve been so blessed to have had the opportunity of getting to know different communities and faiths around the world and be inspired by different ones. Zakat is very inspiring and something I practice in my life. Even though I am a Hindu and an American, I allocate 5 percent of my income after tax to charity and to civic causes every year.
While zakat and sadaqah are particular elements of the Muslim faith, there’s great consistency between zakat and sadaqah and tithing. This culture of giving presents a tremendous opportunity to fund gaps in global humanitarian health crises and ensure help is directed to where it is most needed. I think the tradition of giving in faiths can inspire greater philanthropy, generosity, and collaboration in the future.