DUBAI: What was first identified as another respiratory disease akin to the common flu has taken the lives of over 600,000 people around the world in just six months.
The latest strain of the coronavirus has been described as an invisible enemy, slowly revealing new symptoms as the global scientific community continues investigations into it.
Since the first outbreak of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19), traced to a wet market in Wuhan, China, in late 2019, the infection quickly developed into a full-fledged pandemic, with over 15 million cases reported to date. Symptoms have multiplied, leaving puzzled experts determined to find a cure.
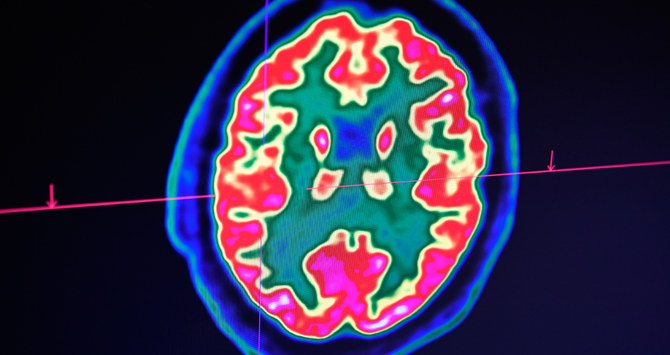
Findings published this month appear to confirm growing concerns about the infection’s link to serious and potentially fatal brain disorders as well as cardiovascular complications.
Chief Scientific Officer Dr. Jeff Drew carries out research into the virus at the Stabilitech laboratory in the UK. (AFP)
“We’re seeing things in the way COVID-19 affects the brain that we haven’t seen before with other viruses,” said Michael Zandi, a consultant neurologist at the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery in London, after the publication of new research in the scientific journal Brain.
Common flu-like signs such as fever, dry cough and sore throat were the first set of symptoms reported at the start of the pandemic. However, the list rapidly expanded to include shortness of breath, loss of taste and smell, nausea and several more symptoms just months later.
Today, the biggest concern among health professionals is the virus’ insidious impact on the brain, with more than 300 studies of COVID-19 patients worldwide showing neurological abnormalities.
One study published in Brain involving 43 patients — 24 males and 19 females — confirmed a range of neurological complications in mildly affected and recovering patients.
Commenting on the new findings, Gregory Poland, an infectious diseases and vaccine expert at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, said the virus’ impact on the brain is “variable” and can range from having no visible impact to causing “large vessel occlusions,” known more commonly as “very large strokes.”
With the virus refusing to discriminate based on age or color, severe cases have been reported among young and relatively healthy individuals as well as those with pre-existing conditions and the elderly.
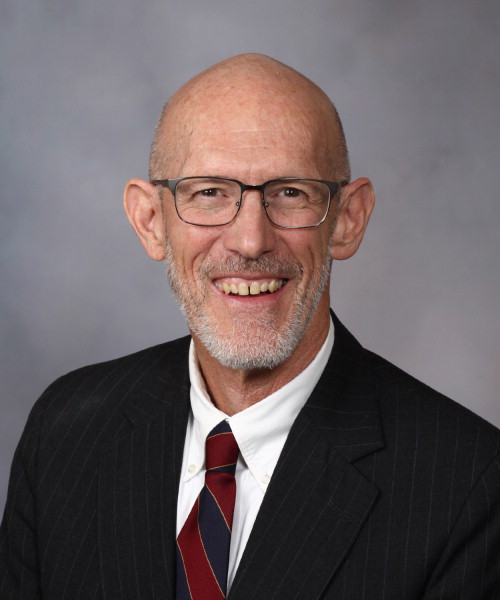

Gregory Poland, an infectious diseases and vaccine expert at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota
“Obviously, the risk goes higher the more severe the disease; large vessel occlusions in young people have occurred with moderate to severe COVID-19 cases. But it can happen to people anywhere along that spectrum,” Poland told Arab News.
In the neurologic realm, the study’s findings showed that patients suffered from encephalopathy; stroke; inflammation of the central nervous system; peripheral nerve problems; cognitive and mental health issues, with delirium, psychosis and several cases of Guillain-Barre syndrome, an immune reaction that attacks the nerves and causes paralysis.
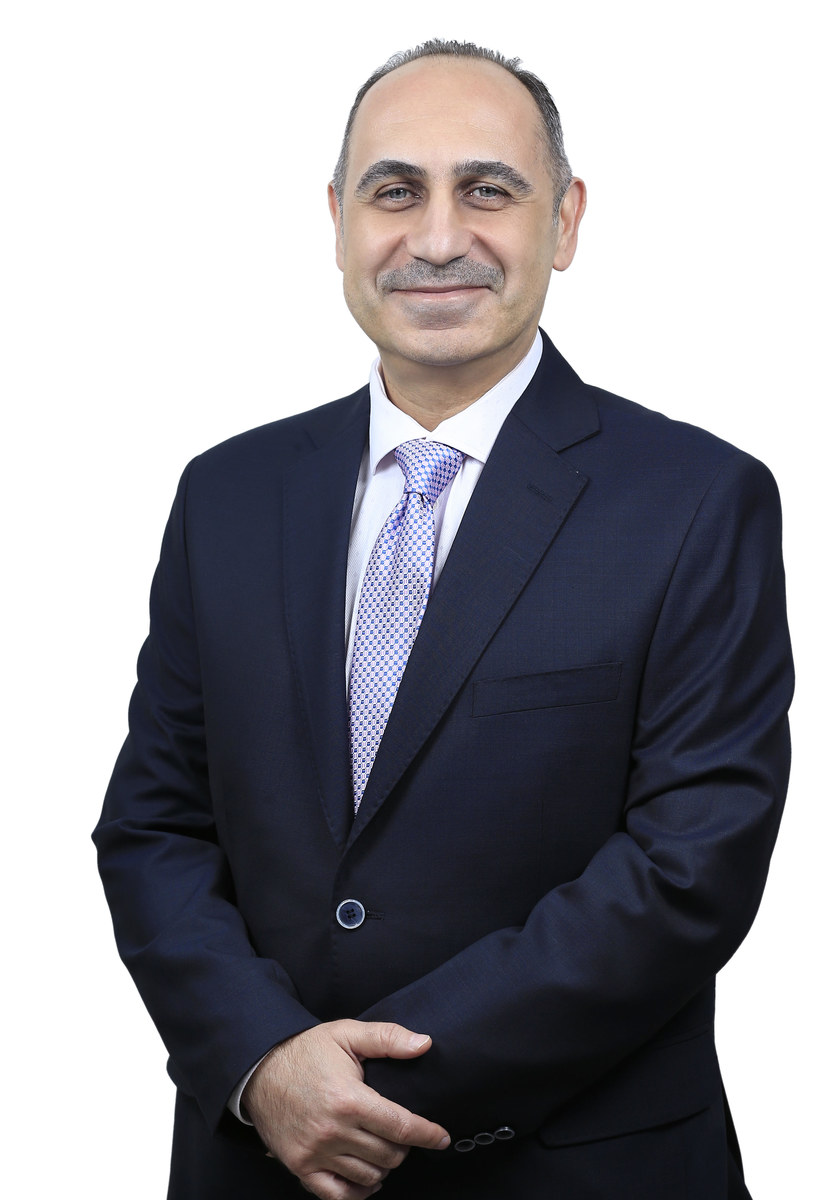

Dr. Taoufik Al-Saadi, chief medical officer and chair of the Neurology Department at the American Center of Psychiatry and Neurology in the UAE
Other symptoms included depression, anxiety and brain fog as well as a loss of smell, taste and sleep in mild and asymptomatic patients.
Another study, “Neurological associations of COVID-19,” published on the Lancet Neurology website, confirmed that a growing number of case reports and series from around the world described the same array of neurological manifestations, noting the virus is of a scale not seen since the 1918 influenza pandemic.
According to Poland, “health care systems are recognizing that there’s going to be a greatly enhanced need for rehabilitation and recovery centers after the COVID-19 pandemic” as a result of the latest outcomes.
His views are echoed by Dr. Taoufik Al-Saadi, chief medical officer and chair of the Neurology Department at the American Center of Psychiatry and Neurology in the UAE, who pointed out that although most individuals are inclined to experience a mild or asymptomatic disease course, some have required ventilatory support.
Data suggest that “one in five infected individuals are hospitalized, and one in 10 individuals are admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU), requiring ventilatory support, due to acute illness in response to this infection,” he said.

“The main issue in survivors of these cases is the physical, cognitive and mental impairment that may persist for several years beyond hospital discharge. Indeed, 80 percent of ICU survivors with confirmed COVID-19 may follow that course,” Al-Saadi told Arab News.
Cases of memory impairment, depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress-like disorders have all been reported in up to 30 percent of these patients and may last up to several years following hospital discharge, said Al-Saadi.
“These complications would certainly affect survivors of this disease in all aspects of their everyday life whether functioning at work, home or in the social sphere,” he said.
Additionally, cognitive, physical and mental problems could result in chronic pain conditions, further causing sleep disorders, which could ultimately affect the overall quality of life. What frightens the scientific community even more is that the long-term impact of such neurological effects has not yet been determined.
However, the virus’ potential long-term health effects do not stop at causing damage to the brain. Scientists are increasingly recognizing the cardiovascular side effects of the virus, with reports of markers of cardiac injury even in young people.
According to Poland, cases of COVID-19 have resulted in inflammation of the heart (myocarditis), decreased heart-muscle function (cardiomyopathy), irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) and dilation of coronary and other blood vessels due to vascular inflammation as well as blood clots.
For patients with a prior history of cardiovascular disorders and increased risk factors, such as hypertension and diabetes, chances of heart complications significantly rise when infected with COVID-19.

The British Heart Foundation confirms these findings, noting that this strain of the virus has been found to increase the risk of blood clotting or thrombosis, leading to cardiovascular problems and, in some cases, organ failure.
The term “COVID toe” has also been coined in reference to painful red or purple swollen patches on the feet, usually the toes of infected patients, a condition known as Chilblains and typically associated with exposure to cold weather.
Some experts have linked COVID toe to blood clots and other neurological issues caused by the virus.
Examining the plethora of symptoms and conditions triggered by the virus, Poland believes experts must not yet discuss the long-term health effects of COVID-19 on patients as research is still in its infancy.
“What we can say is that early indicators of pulmonary fibrosis and scarring are irreversible. We have seen myocarditis and cardiomyopathy, some of which can improve, but we don’t know if they will completely improve,” he said.
 Poland also referred to a group of patients he calls the “long-haulers” who have developed “almost a chronic fatigue-like symptom” accompanied by an assortment of symptoms as result of infection with the virus. For these patients, the virus’ impact is long-lasting.
Poland also referred to a group of patients he calls the “long-haulers” who have developed “almost a chronic fatigue-like symptom” accompanied by an assortment of symptoms as result of infection with the virus. For these patients, the virus’ impact is long-lasting.
Evidence of kidney and liver damage has also been reported in cases around the world, with no clear indication of the long-term consequences.
Similarly, the impact of COVID-19 on pregnant women and their unborn children is yet to be defined with certainty.
With science yet to answer so many questions, Poland’s prognostication is no more reassuring than the available findings on virus. “My guess,” he said, “is that young, healthy people will recover, and older people will have a more difficult time getting back to baseline, if at all.”
--------
Twitter: @jumana_khamis