LONDON: John Hume, the visionary politician who won a Nobel Peace Prize for fashioning the agreement that ended violence in his native Northern Ireland, has died at 83, his family said Monday.
The Catholic leader of the moderate Social Democratic and Labour Party, Hume was seen as the principal architect of Northern Ireland’s 1998 peace agreement. He shared the prize later that year with the Protestant leader of the Ulster Unionist Party, David Trimble, for their efforts to end the sectarian violence that plagued the region for three decades and left more than 3,500 people dead.
“I want to see Ireland as an example to men and women everywhere of what can be achieved by living for ideals, rather than fighting for them, and by viewing each and every person as worthy of respect and honor,” he said in 1998. “I want to see an Ireland of partnership, where we wage war on want and poverty, where we reach out to the marginalized and dispossessed, where we build together a future that can be as great as our dreams allow.”
Hume died Monday morning after suffering from ill health for several years, his family said.
Born on Jan. 18, 1937, in Northern Ireland’s second city — Londonderry to British Unionists, Derry to Irish nationalists — Hume trained for the priesthood before becoming a fixture on Northern Ireland’s political landscape. An advocate of nonviolence, he fought for equal rights in what was then a Protestant-ruled state, but he condemned the Irish Republican Army because of his certainty that no injustice was worth a human life.
Although he advocated for a united Ireland, Hume believed change could not come to Northern Ireland without the consent of its Protestant majority. He also realized that better relations needed to be forged between Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland and between London and Dublin.
He championed the notion of extending self-government to Northern Ireland with power divided among the groups forming it.
“Ireland is not a romantic dream; it is not a flag; it is 4.5 million people divided into two powerful traditions,″ he said. “The solution will be found not on the basis of victory for either, but on the basis of agreement and a partnership between both. The real division of Ireland is not a line drawn on the map, but in the minds and hearts of its people.”
While both Hume and Trimble credited the people of Northern Ireland and the Irish Republic for approving a referendum that led to power sharing, it was Hume’s diplomacy that offered the impetus to the peace process that led to the 1998 Good Friday accord.
Hume won the breakthrough in Belfast’s political landscape in 1993 by courting Gerry Adams, the head of Sinn Fein, the political wing of the Irish Republican Army, in hopes of securing an IRA cease-fire. That dialogue burnished Adams’ international credibility and led to two IRA cease-fires in 1994 and 1997.
Like most Protestant politicians at the time, Trimble had opposed efforts to share power with Catholics as something that would jeopardize Northern Ireland’s union with Britain. He at first refused to speak directly with Adams, insisting that IRA commanders needed to prove they were willing to abandon violence.
He ultimately relented and became pivotal in peacemaking efforts.
Hume had envisioned a broad agenda for the discussions, arguing they must be driven by close cooperation between the British and Irish governments. The process was overseen by neutral figures like US mediator George Mitchell, with the decisions overwhelmingly ratified by public referendums in both parts of Ireland.
“Without John Hume, there would not have been a peace process,” Mitchell said at the time the prize was announced. ”Without David Trimble, there would not have been a peace agreement.”
Hume and Trimble were said to have had a frosty relationship. But Trimble on Monday described a thawing after the Nobel ceremony in Oslo, recalling that the hotel at which they were staying had suggested the two men chose to relax away from each other.
“We didn’t do that. We relaxed and in some sense celebrated the occasion jointly, and that for me spelt out the principle for how we were going to proceed in the years after that,” he told the BBC.
Tributes poured in after’s Hume’s death was announced, including praise from Adams, who called him a “giant in Irish politics.” Former Prime Minister Tony Blair, who was in office at the time the accord was signed, lauded Hume’s “epic” contribution to the peace process.
Former US President Bill Clinton and former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton issued a statement describing their sadness.
“Through his faith in principled compromise, and his ability to see his adversaries as human beings, John helped forge the peace that has held to this day,” they said.
UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson said the Northern Ireland of today is Hume’s legacy.
“He stood proudly in the tradition that was totally opposed to violence and committed to pursuing his objectives by exclusively peaceful and democratic means,” Johnson said on Twitter. “His vision paved the way for the stability, positivity and dynamism of the Northern Ireland of today and his passing is a powerful reminder of how far Northern Ireland has come.”
Hume’s family said his funeral would be in keeping with strict guidelines on attendees because of the COVID-19 pandemic. A memorial will be arranged later.
“We are grateful for your condolences and support, and we appreciate that you will respect the family’s right to privacy at this time of great loss,” the family said in a statement. “It seems particularly apt for these strange and fearful days to remember the phrase that gave hope to John and so many of us through dark times: ‘We shall overcome.’”
John Hume, who worked to end N. Ireland violence, dies at 83
https://arab.news/vdj9x
John Hume, who worked to end N. Ireland violence, dies at 83

- Although he advocated for a united Ireland, Hume believed change could not come to Northern Ireland without the consent of its Protestant majority
- John Hume: I want to see Ireland as an example to men and women everywhere of what can be achieved by living for ideals, rather than fighting for them
Efforts underway to bring home Filipinos killed in UAE floods
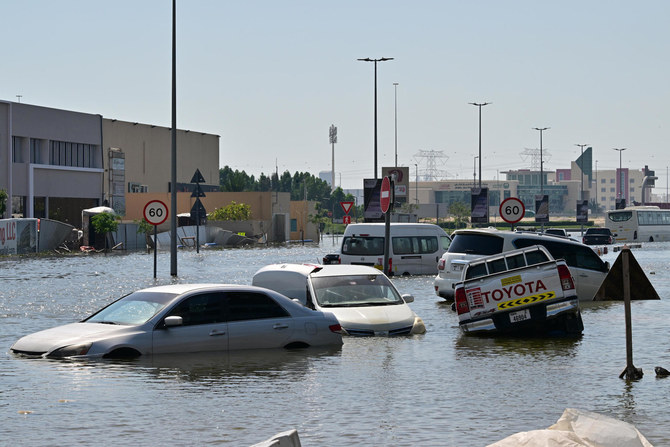

- At least three Filipinos lost their lives in the unprecedented flooding
- Philippine consulate received assistance requests from at least 100 Filipinos
Manila: The Philippine government is assisting Filipinos affected by the record-high rains and flooding that hit the UAE this week, authorities said on Saturday, as it works to repatriate the nationals who lost their lives.
A strong storm first hit Oman last weekend, killing at least 20 people, before it pounded the UAE on Tuesday, marking the heaviest rains in 75 years and bringing the Gulf state to a standstill.
The Philippine Department of Migrant Workers has confirmed the deaths of at least three Filipinos who died in road accidents as their vehicles were submerged in floodwaters.
Philippine Consul General Marford Angeles told Arab News the consulate had received assistance requests from at least 100 Filipinos — some working in the UAE, some studying, and some transiting via Dubai.
“Over 1 million Filipino nationals are currently residing in the UAE ... Majority of assistance requests received by the consulate so far originate from the populous emirates of Dubai and Sharjah, reflecting the concentration of Filipino residents in these areas,” he said.
“The unprecedented weather conditions in the UAE affected most residents.”
The three Filipinos who lost their lives in the floods were two women who died inside their flooded vehicle, and a man who died after sustaining major injuries when his vehicle fell into a sinkhole. His two passengers have been hospitalized.
“The Department of Migrant Workers, through its Migrant Workers Offices in Dubai and Abu Dhabi, is working with local authorities for the repatriation of the remains of three overseas Filipino workers (OFWs) who died during the severe flooding,” the DMW said in a statement.
“Two other OFWs, both male, suffered injuries from the vehicular accident that happened in the sinkhole. They are recuperating from their injuries.”
US House to vote on long-awaited $95 billion Ukraine, Israel aid package

- Some hard-line Republicans have voiced strong opposition to further Ukraine aid
WASHINGTON: The Republican-controlled US House of Representatives on Saturday is set to vote on, and expected to pass, a $95 billion legislative package providing security assistance to Ukraine, Israel and Taiwan, over bitter objections from party hard-liners.
More than two months have passed since the Democratic-majority Senate passed a similar measure and US leaders from Democratic President Joe Biden to top Senate Republican Mitch McConnell have been urging embattled House Speaker Mike Johnson to bring it up for a vote.
Johnson this week chose to ignore ouster threats by hard-line members of his fractious 218-213 majority and push forward the measure that includes some $60.84 billion for Ukraine as it struggles to fight off a two-year Russian invasion.
The unusual four-bill package also includes funds for Israel, security assistance for Taiwan and allies in the Indo-Pacific and a measure that includes sanctions, a threat to ban the Chinese-owned social media app TikTok and the potential transfer of seized Russian assets to Ukraine.
“The world is watching what the Congress does,” the White House said in a statement on Friday. “Passing this legislation would send a powerful message about the strength of American leadership at a pivotal moment. The Administration urges both chambers of the Congress to quickly send this supplemental funding package to the President’s desk.”
A bipartisan 316-94 House majority on Friday voted to advance the bill to a vote, and Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer told senators to be ready to work over the weekend if it passes the House as expected.
“It’s not the perfect legislation, it’s not the legislation that we would write if Republicans were in charge of both the House, the Senate, and the White House,” Johnson told reporters on Friday. “This is the best possible product that we can get under these circumstances to take care of these really important obligations.”
Some hard-line Republicans have voiced strong opposition to further Ukraine aid, with some arguing the US can ill afford it given its rising $34 trillion national debt. They have repeatedly raised the threat of ousting Johnson, who became speaker in October after his predecessor, Kevin McCarthy, was ousted by party hard-liners.
Representative Bob Good, chair of the hard-line House Freedom Caucus, told reporters on Friday that the bills represent a “slide down into the abyss of greater fiscal crisis and America-last policies that reflect Biden and Schumer and (House Democratic leader Hakeem) Jeffries, and don’t reflect the American people.”
But Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump, who carries huge influence in the party, on April 12 voiced support for Johnson and in a Thursday social media post said Ukraine’s survival is important for the US
The bills provide $60.84 billion to address the conflict in Ukraine, including $23 billion to replenish US weapons, stocks and facilities; $26 billion for Israel, including $9.1 billion for humanitarian needs, and $8.12 billion for the Indo-Pacific.
AI’s relentless rise gives journalists tough choices
- AI tools imitating human intelligence are used to transcribe sound files, summarize texts and translate
- Columbia University teacher says collaborating with AI “tempting” in the face of increasingly right media resources
PERUGIA, Italy: The rise of artificial intelligence has forced an increasing number of journalists to grapple with the ethical and editorial challenges posed by the rapidly expanding technology.
AI’s role in assisting newsrooms or transforming them completely was among the questions raised at the International Journalism Festival in the Italian city of Perugia that closes on Sunday.
AI tools imitating human intelligence are widely used in newsrooms around the world to transcribe sound files, summarize texts and translate.
In early 2023, Germany’s Axel Springer group announced it was cutting jobs at the Bild and Die Welt newspapers, saying AI could now “replace” some of its journalists.
Generative AI — capable of producing text and images following a simple request in everyday language — has been opening new frontiers as well as raising concerns for a year and a half.
One issue is that voices and faces can now be cloned to produce a podcast or present news on television. Last year, Filipino website Rappler created a brand aimed at young audiences by converting its long articles into comics, graphics and even videos.
Media professionals agree that their trade must now focus on tasks offering the greatest “added value.”
“You’re the one who is doing the real stuff” and “the tools that we produce will be an assistant to you,” Google News general manager Shailesh Prakash told the festival in Perugia.
The costs of generative AI have plummeted since ChatGPT burst onto the scene in late 2022, with the tool designed by US start-up OpenAI now accessible to smaller newsrooms.
Colombian investigative outlet Cuestion Publica has harnessed engineers to develop a tool that can delve into its archives and find relevant background information in the event of breaking news.
But many media organizations are not making their language models, which are at the core of AI interfaces, said University of Amsterdam professor Natali Helberger. They are needed for “safe and trustworthy technology,” he stressed.
According to one estimate last year by Everypixel Journal, AI has created as many images in one year as photography in 150 years.
That has raised serious questions about how news can be fished out of the tidal wave of content, including deepfakes.
Media and tech organizations are teaming up to tackle the threat, notably through the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity, which seeks to set common standards.
“The core of our job is news gathering, on-the-ground reporting,” said Sophie Huet, recently appointed to become global news director for editorial innovation and artificial intelligence at Agence France-Presse.
“We’ll rely for a while on human reporters,” she added, although that might be with the help of artificial intelligence.
Media rights watchdog Reporters Without Borders, which has expanded its media rights brief to defending trustworthy news, launched the Paris Charter on AI and journalism late last year.
“One of the things I really liked about the Paris Charter was the emphasis on transparency,” said Anya Schiffrin, a lecturer on global media, innovation and human rights at Columbia University in the United States.
“To what extent will publishers have to disclose when they are using generative IA?“
Olle Zachrison, head of AI and news strategy at public broadcaster Swedish Radio, said there was “a serious debate going on: should you mark out AI content or should people trust your brand?“
Regulation remains in its infancy in the face of a constantly evolving technology.
In March, the European Parliament adopted a framework law aiming to regulate AI models without holding back innovation, while guidelines and charters are increasingly common in newsrooms.
AI editorial guidelines are updated every three months at India’s Quintillion Media, said its boss Ritu Kapur.
None of the organization’s articles can be written by AI and the images it generates cannot represent real life.
AI models feed off data, but their thirst for the vital commodity has raised hackles among providers.
In December, the New York Times sued OpenAI and its main investor Microsoft for violation of copyright.
In contrast, other media organizations have struck deals with OpenAI: Axel Springer, US news agency AP, French daily Le Monde and Spanish group Prisa Media whose titles include El Pais and AS newspapers.
With resources tight in the media industry, collaborating with the new technology is tempting, explained Emily Bell, a professor at Columbia University’s journalism school.
She senses a growing external pressure to “Get on board, don’t miss the train.”
Fighting flares at Myanmar-Thai border as rebels target stranded junta troops
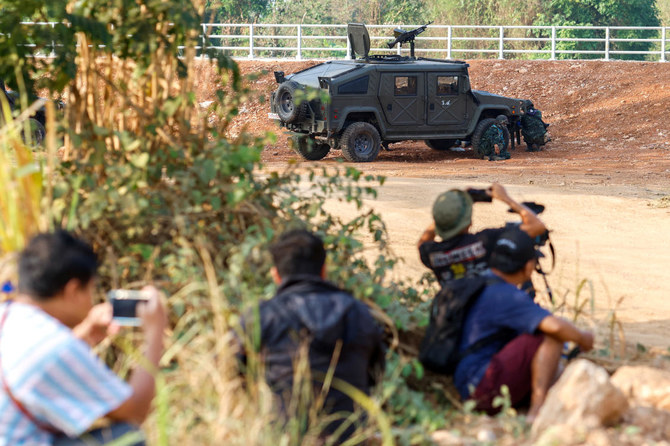

- Resistance fighters and ethnic minority rebels seized the key trading town of Myawaddy on the Myanmar side of the frontier on April 11
Fighting raged at Myanmar’s eastern frontier with Thailand on Saturday, witnesses, media and Thailand’s government said, forcing about 200 civilians to flee as rebels pressed to flush out junta troops holed up for days at a bridge border crossing.
Resistance fighters and ethnic minority rebels seized the key trading town of Myawaddy on the Myanmar side of the frontier on April 11, dealing a big blow to a well-equipped military that is struggling to govern and is now facing a critical test of its battlefield credibility.
Three witnesses on the Thai and Myanmar sides of the border said they heard explosions and heavy machine gun fire near a strategic bridge from late on Friday that continued into early Saturday.
Several Thai media outlets said about 200 people had crossed the border to seek temporary refuge in Thailand.
Thai broadcaster NBT in a post on social media platform X said resistance forces used 40-milimeter machine guns and dropped 20 bombs from drones to target an estimated 200 junta soldiers who had retreated from a coordinated rebel assault on Myawaddy and army posts since April 5.
Reuters could not immediately verify the reports and a Myanmar junta spokesperson could not immediately be reached for comment.
Thai Prime Minister Srettha Thavisin said he was closely monitoring the unrest and his country was ready to provide humanitarian assistance if necessary.
“I do not desire to see any such clashes have any impact on the territorial integrity of Thailand and we are ready to protect our borders and the safety of our people,” he said on X. He made no mention of refugees.
BIG SETBACK
Myanmar’s military is facing its biggest challenge since first taking control of the former British colony in 1962, caught up in multiple, low-intensity conflicts and grappling to stabilize an economy that has crumbled since a 2021 coup against Nobel laureate Aung San Suu Kyi’s government.
The country is locked in a civil war between the military on one side and, on the other, a loose alliance of established ethnic minority armies and a resistance movement born out of the junta’s bloody crackdown on anti-coup protests.
The capture of Myawaddy and surrounding army outposts is a significant setback for a junta that has been squeezed by Western sanctions, with the town a key tax revenue source and conduit for more than $1 billion of annual border trade.
The Khaosod newspaper in a post on X showed a video of Myanmar civilians, many of them women and children, being marshalled by Thai soldiers at an entry point to Thailand.
Thailand had on Friday said no refugees had entered the country and it was discussing with aid agencies about increasing humanitarian relief to civilians on the Myanmar side.
Taiwan’s defense ministry detects 21 Chinese military aircraft

- The median line bisects the Taiwan Strait, a narrow 180-kilometer waterway separating the island from mainland China
TAIPEI: Taipei’s defense ministry said it had detected 21 Chinese military aircraft around the self-ruled island since 8:15 am (0015 GMT) on Saturday, a month before Taiwan’s May 20 inauguration of incoming president Lai Ching-te.
“17 aircraft (of the 21) crossed the median line and its extension, entered our northern, central, and southwestern (air defense identification zone), and joined PLA vessels for joint combat patrol,” it said in a statement posted on X around 11:30 am.
Taiwan’s armed forces “are monitoring the activities with our joint surveillance systems, and have dispatched appropriate assets to respond accordingly.”
The median line bisects the Taiwan Strait, a narrow 180-kilometer waterway separating the island from mainland China.
Beijing does not recognize the line as it claims democratic Taiwan as part of its territory. It has also never renounced the use of force to bring the island under its control.
China sends warplanes and naval vessels around Taiwan on a near daily basis — a move experts say is a form of “grey-zone harassment,” stopping short of an outright act of war but enough to exhaust Taipei’s armed forces.
According to the defense ministry, the 21 aerial objects detected Saturday included J-16 fighter jets and Y-8 medium-range transport aircraft, as well as drones.
The highest number around Taiwan so far this year was in March, when the ministry said 36 Chinese aircraft were detected in a single 24-hour period.
Last year’s record was in September when Beijing’s military sent 103 aircraft — 40 of which crossed the median line — in a 24-hour period.
Saturday’s show of force comes a day after China activated two aviation routes that run close to Taiwan’s outlying islands of Kinmen and Matsu.
Taipei’s Civil Aviation Administration expressed “solemn protest against China’s unilateral measures without consultation” on Friday.
The new routes make the airspace separation between the two sides “very narrow,” it said, increasing flight safety risks during bad weather or abnormal flight operations.
China’s aviation authority also said Friday the airspace around Fuzhou Changle Airport — 30 kilometers from the closest outlying Taiwanese island — would be “further optimized and adjusted” on May 16, four days before the inauguration.
Under the administration of Taiwanese President Tsai Ing-wen, tensions between Beijing and Taipei have ramped up, as she and her government do not acknowledge China’s claim.
Her deputy, Vice President Lai, won elections in January despite warnings from Beijing that he would be the cause of “war and decline” for Taiwan.
China regards Lai — who used to be outspoken about Taiwan independence — as a “dangerous separatist,” though he has moderated his views in recent years.




















