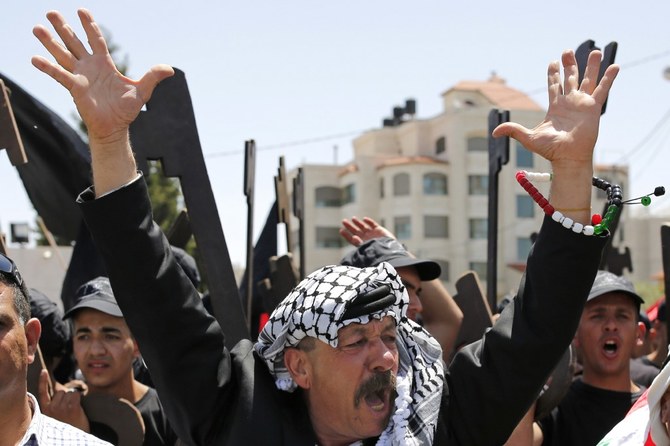
This week, Palestinians commemorate the 71st anniversary of The Nakba (Catastrophe) of 1948. The long night is getting darker and darker, with not a sliver of light in sight.
Many peace plans have been proposed since then, but they have all failed to bring about an end to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. There is no reason to believe President Donald Trump’s much-talked-about “deal of the century” will be any different.
Palestinian leaders are reluctant to accept a compromise that does not include the sharing of Jerusalem and a full and complete return to the “The Green Line,” the 1949 armistice borders that defined Israel until 1967.
For its part, Israel has been reluctant to accept a sovereign, independent Palestine state in the occupied territories and has continued to expand its confiscation of Palestinian-owned lands to build settlements exclusively for Jewish settlers, who are armed and violent.
The issue of Palestinian statehood came up peripherally when Egypt’s Anwar Sadat made his dramatic gesture in 1977 to recognize Israel in exchange for peace, and in 1993, when Yitzhak Rabin, the Israeli leader, and Yasir Arafat, the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) chairman, signed the Oslo Accords.
Barring those two moments, nearly every peace effort has failed and ended up adding to the suffering of Palestinians. The Nakba has only worsened, becoming an “Akbar Nakba” (Greater Catastrophe) that Palestinians have become used to.
In 1949, Israel and the Arab states reached an armistice, which is basically a suspension of conflict. Although Israel defined its borders (the Green Line) on its own, the armistice never recognized final borders.
In 1967, when the Arab bluff was called by an Israel invasion of the West Bank, East Jerusalem, the Gaza Strip, Egypt’s Sinai, and Syria’s Golan Heights, the UN stepped in. It approved Security Council Resolution 242, which called for recognition of all the countries of the region (including Israel) and, as an afterthought, urged “a just resolution of the refugee problem.”
UN Resolution 242 became the basis for peace talks between Israel, Egypt and Jordan, but not between Israelis and Palestinians, who were compelled to take matters into their own hands by setting up the PLO and launching a revolution to free their occupied homeland.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
Even the meaning of Resolution 242 was distorted to exclude Palestinian statehood. Palestinians were relegated to the status of “a refugee problem,” their claims and rights countered by Israeli assertions that Jews who immigrated to Israel - and were living in former Arab homes and on Arab-owned lands - were refugees too.
Resolution 242 was adopted unanimously by the Security Council and embraced by Egypt and Jordan, but the larger UN General Assembly never had a direct say in its adoption. After the Six Day War of 1967, General Yigal Allon, Israel’s labor minister, floated a bold peace plan, but it was rejected by everyone.
After 1977, Sadat was feted as a “peacemaker” by the West for his to visit Jerusalem and address the Knesset. The following year he signed a peace accord with Menachem Begin, the Israeli prime minister who began his career as a leader of the violent Jewish underground organization Irgun Zvai Leumi.
Sadat believed the Camp David agreement would serve as a framework for peace with Jordan, Syria and the Palestinians. However, Begin never entered into serious negotiations with the Palestinians.
In December 1987, Palestinians rebelled against Israel’s occupation when an Israeli jeep ran over four Palestinian civilians and a teenager was killed during a subsequent protest. It was the first Intifada (uprising).
As the civilian population revolted against Israel’s military, the two rival Palestinian factions - the Gaza Strip’s Islamic Association, led by Sheikh Ahmed Yassin, a wheelchair-bound quadriplegic, and the exiled PLO leadership in Tunis - saw the situation as a zero-sum game. The Islamic Association launched a military force called Hamas, which was described in a BBC interview as “a paramilitary wing” of the Palestinian Muslim Brotherhood.
Meanwhile, the PLO had launched an initiative to win international backing for its leadership as the “sole representatives of the Palestinian people.” Soon, it had opened dialogue through intermediaries with Israel.
In 1988, US President Ronald Reagan issued a presidential waiver to allow the opening of formal discussions with PLO officials. Israel, which designated the PLO as a “terrorist organization,” dropped the designation following the Madrid Conference in 1991.
That led Arafat to recognize Israel’s “right to exist” and open the first substantive peace talks to create a Palestine state with Rabin. However, Rabin was assassinated at the conclusion of a rally in Tel Aviv in November 1995 by Yigal Amir, a Jewish extremist.
As part of the Oslo process, Jordan’s King Hussein signed a peace accord with Israel in 1979, leaving Palestine’s destiny in the hands of Arafat and the Palestine National Authority, which tried to set up a base in Gaza to counter the rising political presence of Hamas.
Meanwhile, pro-peace activists in Israel tried unsuccessfully to revive the peace process after Rabin was murdered. US President Bill Clinton, who got Rabin and Arafat to shake hands on the White House lawn in September 1993, was desperate to achieve any kind of peace. He had arranged for negotiations between Arafat and Israeli’s new prime minister, Ehud Barak, through Dennis Ross, a US diplomat.
In the 1999 vote Barak had trounced Likud’s Benjamin Netanyahu, who had prevailed over Shimon Peres, the veteran Labor politician, in elections three years earlier. Barak, with Clinton’s help, tried to restore the peace process. However, Arafat balked at a final agreement on one issue: the demand that Palestinians abandon the “Right of Return.”
As luck would have it, Barak lost the February 2001 election to Ariel Sharon, the Likud politician who stirred up a storm by entering the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound in September 2000 accompanied by thousands of Israeli security personnel.
In 2002, European leaders and Israel’s leftist opposition appealed for a “road map to peace”, but Sharon and Netanyahu refused to deal with Arafat, choosing to keep the veteran Palestinian leader under siege until his death on November 11, 2004.
Between December 2006 and September 2008, Ehud Olmert, the new Israeli prime minister, held talks with Arafat’s successor Mahmoud Abbas, but the duo failed to achieve a breakthrough despite the support of US President Barack Obama. The dialogue came to an end when Netanyahu was elected prime minister in 2009.
Netanyahu opposes the idea of a two-state solution and the creation of a Palestinian state. But the process that could have led to such an outcome is all but dead. These days Netanyahu seeks to achieve peace with the Arab world but not with Palestinians.