AL-JAHRA, Kuwait: On the outskirts of Kuwait City, the love Kuwaitis have for former US President George H.W. Bush could be seen in 2016 on a billboard one Bedouin family put up to announce their son’s wedding.
That son being Bush Al-Widhan, born in the aftermath of the 1991 Gulf War that saw US-led forces expel the occupying Iraqi troops of dictator Saddam Hussein.
“He was a real man, a lion,” said Mubarak Al-Widhan, the father of the Kuwaiti Bush, of the American president. “He stood for our right for freedom, and he gave us back our country.”
With Bush’s death , his legacy across the Middle East takes root in that 100-hour ground war that routed Iraqi forces. That war gave birth to the network of military bases America now operates across the Arabian Gulf supporting troops in Afghanistan and forces fighting against Daesh in Iraq and Syria.
However, Bush ultimately would leave the Shiite and Kurdish insurgents he urged to rise up against Saddam in 1991 to face the dictator’s wrath alone, leading to thousands of deaths. That mixed picture only extends to the presidency of his son, George W. Bush, who ordered the 2003 US-led invasion of Iraq that overthrew Saddam, whom he once famously described as “the guy who tried to kill my dad one time.”
“I feel tension in the stomach and in the neck ... but I also feel a certain calmness when we talk about these matters,” the elder Bush once said about the 1991 Gulf War, according to biographer Jon Meacham. “I know I am doing the right thing.”
Iraq invaded Kuwait on Aug. 2, 1990, angry that the tiny neighbor and the United Arab Emirates had ignored OPEC quotas, which Saddam claimed cost his nation $14 billion. Saddam also accused Kuwait of stealing $2.4 billion by pumping crude from a disputed oil field and demanded that Kuwait write off an estimated $15 billion of debt that Iraq had accumulated during its 1980s war with Iran.
A World War II fighter pilot shot down fighting against the Japanese, Bush came to view Saddam as similar to Adolf Hitler, a madman who seized neighboring Kuwait and could plunge the world into conflict if he continued into Saudi Arabia. With Vietnam still a potent memory, Bush rallied together a coalition of nations to back the US as it deployed troops to the region and began bombing runs. He talked Israel out of retaliating for Iraqi Scud missiles attacks for fear of alienating Arab allies.
“This will not stand. This will not stand, this aggression against Kuwait,” Bush famously warned.
And it didn’t.
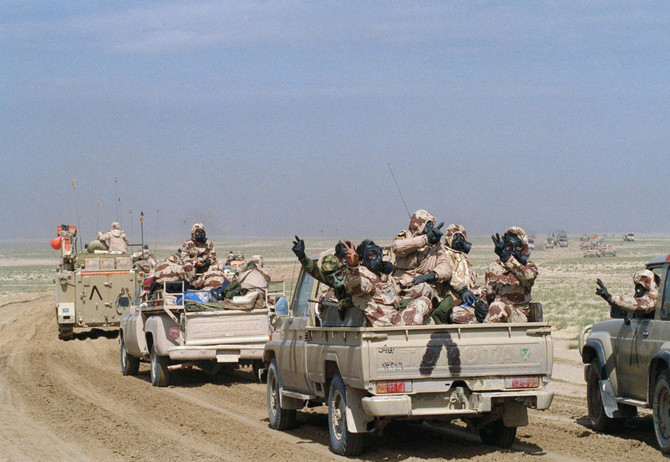
On Feb. 24, 1991, US troops and their allies stormed into Kuwait. It ended 100 hours later. America suffered only 148 combat deaths during the whole campaign, while over 20,000 Iraqi soldiers were killed.
In the aftermath of the campaign, some called for Bush to continue into Iraq and topple Saddam. Bush in speeches encouraged Iraqis to rise up against the dictator, while privately hoping someone within his own military would depose him.
“To occupy Iraq would shatter our coalition, turning the whole Arab world against us, and make a broken tyrant into a latter-day Arab hero,” Bush later said. “It would have taken us way beyond the imprimatur of international law, ... assigning young soldiers to a fruitless hunt for a securely entrenched dictator and condemning them to fight in what would be an unwinnable urban guerrilla war.”
That hesitation allowed Saddam to regain the upper hand against insurgents and caused a refugee crisis in Iraq’s northern Kurdish region. The dictator tauntingly installed a tile mosaic of a scowling likeness of the president at the door of Baghdad’s Al-Rashid Hotel, which forced entering foreign dignitaries to often step on his face just above its “Bush is criminal” caption.
Even Iran, which hated Saddam for starting their 1980s war, remained suspicious of Bush despite his pledge of “good will begets good will.” Iran leaned on Lebanon’s Shiite militants to help win the release American hostages like Terry Anderson of The Associated Press, but relations went no further. One of Bush’s last acts as president, pardoning former Defense Secretary Caspar Weinberger and others for their role in the Iran-Contra scandal, an offshoot of that hostage crisis.
Still, Bush’s decisions in the 1991 war and its aftermath echo even now. The Kurdish crisis gave birth to the US-imposed no-fly zone in northern Iraq that allowed the Kurds to flourish into the semi-autonomous region now demanding independence. Defense agreements with Gulf nations grew into a series of major military installations across the region.
His son would launch the 2003 invasion of Iraq after 9/11 and become so hated in the Arab world an Iraq journalist would even throw a shoe at him during a news conference. But the elder Bush remained beloved, perhaps nowhere more than Kuwait, where Americans even today can get hugged while walking down the street. A group of Kuwaiti officials including the country’s National Assembly speaker met with the former president in October 2017 to wish him well.
The former president’s Kuwaiti namesake Bush Al-Widhan ended up working in the country’s National Guard. His name fascinated others.
“I went with my father to Cleveland, Ohio ... and the passport control clerk asked me about the name,” Al-Widhan recounted. “I couldn’t tell him the story. My English is bad. I said: ‘George Bush, George Bush. Kuwait war.’ Everyone thought it was a great name.”