WASHINGTON: Nature expresses its fury in sundry ways. Two deadly storms — Hurricane Florence and Typhoon Mangkhut — roared ashore on the same day, half a world apart, but the way they spread devastation was as different as water and wind.
Storms in the western Pacific generally hit with much higher winds and the people who live in their way are often poorer and more vulnerable, Princeton University hurricane and climate scientist Gabriel Vecchi said Saturday. That will likely determine the type of destruction.
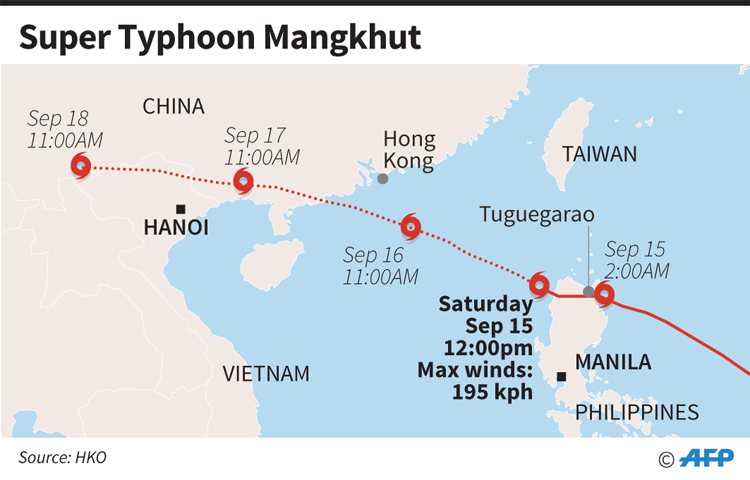
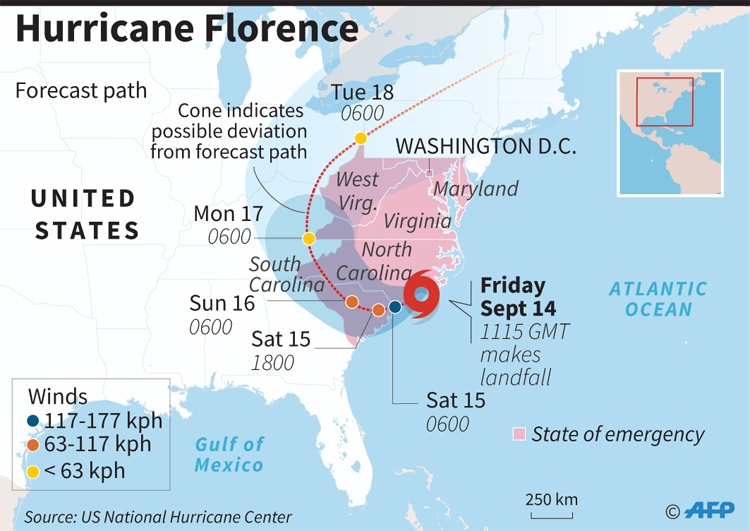
Mangkhut made landfall Friday on the northeastern tip of Luzon island in the Philippines with top-of-the-scale Category 5 winds of 165 mph. Florence had weakened to a Category 1 storm with 90 mph winds by the time it arrived at North Carolina’s coast.
Yet a day after landfall the faster-moving Mangkhut was back out over open water — weakened, but headed across the South China Sea toward China. Florence, meanwhile, was still plodding across South Carolina at a pace slower than a normal person walks. By Saturday morning, it had already dumped more than 30 inches (76 centimeters) of rain, a record for North Carolina.
Experts say Mangkhut may well end up being the deadlier storm. As of Saturday afternoon, the death count in the Philippines was a bit higher, although still far below that of other storms that have hit the disaster-prone island nation. And with Mangkhut now headed toward the densely populated southeast coast of China, it is likely to cause more death and destruction. But Florence’s watery insured damage total will eventually be higher, Ernst Rauch, head of climate research for the world’s largest reinsurer Munich Re, told German media.
That’s because of a combination of geography, climatic conditions and human factors.
The western Pacific has two-and-a-half times more storms that reach the minimum hurricane strength of 74 mph. It has three-and-a-half times more storms that reach major hurricane strength of 111 mph, and three times more accumulated energy out of those hurricanes, an index that measures not just strength and number of storms but how long they last, according to more than 65 years of storm data .
So far this year there have been 23 named storms in the western Pacific and 10 in the Atlantic, both regions more than 30 percent busier than average years. Hurricanes and typhoons are the same type of storm; both are tropical cyclones, but those that occur in the Pacific west of the International Date Line are called typhoons.
The water in the western Pacific is warmer, and warm water fuels storms. There are also only a few pieces of land to get in the way and weaken them, said University of Miami hurricane researcher Brian McNoldy.
“If we are ever going to have a Category 6 (a speculated-on level that’s above current measurement tools), the western Pacific is where it’s going to be,” said meteorologist Ryan Maue of weathermodels.com.
The Philippines tends to get hit nearly every year, the Carolinas far less frequently though with lots of close calls, Maue said. That shows another big difference in the storms. Mangkhut formed further south and stayed south — over warmer water. Florence was out of the tropics when it hit land.
Because of that, Florence was weakened by the dry air and upper level winds of the higher latitudes. Not so the more southerly Mangkhut, which Maue said, “essentially had a perfect environment to intensify to a Category 5 and stay there.”
“Mangkhut and Florence are certainly different animals,” said Colorado State University hurricane researcher Phil Klotzbach. Because Florence is moving so slowly, he said, it will dump more rain than Mangkhut, which is named for the Thai word for the mangosteen fruit.
Both storms have lasted a long time, especially Florence which formed all the way over near Africa 15 days before landfall, McNoldy said. Both storms cover a large area, but Mangkut still dwarfs Florence. Mangkhut’s tropical storm force winds stretched more than 325 miles from the center, while Florence’s spread about 195 miles, Klotzbach said.
Economics also play a role in a storm’s impact. As a developing country, the Philippines is much poorer than the southeastern United States, which means houses tend to be less sturdy and first responders less well equipped, among other factors. This is one reason why, when disaster does strike, the effects can be devastating. In 2013, one of the most powerful storms on record, Typhoon Haiyan , killed 7,300 people and displaced more than 5 million when it swept across the islands of the central Philippines.
Straddling the famous Pacific Ring of Fire, the Philippines is also bedeviled by volcanoes and earthquakes, and while there are considerable patches of poverty in North and South Carolina, it is not the same as the rural area where Mangkhut hit.
Munich Re’s Rauch said about 30 to 50 percent of storm damage is usually insured in the United States but often less than 10 percent in developing countries, meaning nine-tenths of the people hit will end up shouldering a bigger economic burden.
In the United States, “you can’t move houses, but people can move out of the way,” reflecting mounting damages from storms and often lower losses in life, Vecchi said.
As the world warms from the burning of fossil fuels, the globe will see both more extremely intense storms like Mangkhut and wetter storms like Florence, Vecchi said.
































